Introduction
Modern technology has brought about many choices regarding the processing of data to improve business processes. As technology continues to advance, businesses are left with no alternative but to embrace the use of information systems to remain relevant to the needs of the consumers (Nel, 2007). Besides applying information systems to reduce operational costs, businesses may also benefit from improved methods of operation, better services and products, and improved relationships with clients. Figure 1 shows how information systems can add value to a business by providing various services.
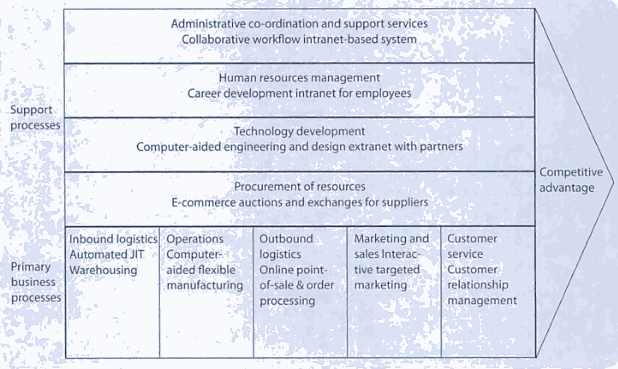
Types of Information Systems
A number of information systems exist to enable businesses improve efficiency and withstand the ever increasing competition in the market. The different types of information systems may be linked to the levels of management seen in most businesses. This is illustrated by table 1.1.
Table 1.1: Level of Management in a Business
The four major types of information systems are:
- Management Information Systems (MIS)
- Decision Support Systems (DSS)
- Transaction Processing Systems (TPS)
- Executive Information Systems (EIS)
Other types of information systems also exist to support the business operations in a number of ways. They include:
- Office Automation Systems (OAS)
- Communication Systems
- Groupware Systems
These systems are explained in the following sub sections.
Transaction Processing Systems
Transaction Processing Systems provide support for the operational level of a business and take care of the most basic operations that happen on a day to day basis. They supply data for the higher levels of management in the business such as the MIS and the EIS.
Management Information Systems (MIS)
According to Nel (2007), a Management Information System may be defined in terms of its application to the different classes of decisions. An MIS will support the process of making unstructured or semi-structured decisions by performing some of the phases of the decision making process and providing supporting information for other phases. An MIS is made up of two components that support the decision process. These are the structured decision system (SDS) that deals with structured decisions and the decision support system (DSS) that supports the unstructured and semi-structured decisions (Nel, 2007).
Decision Support Systems (DSS)
The primary purpose of a decision support system is to provide the manager with the necessary information that will allow him or her to make intelligent business decisions (Nel, 2007). A DSS is also regarded as a specialized MIS that supports a manager’s skills at all stages of decision making. It helps to identify the problem, choose relevant data, select the approach to be used in making the decision and evaluate alternative courses of action (Nel, 2007).
Executive Information Systems (EIS)
These systems are also referred to as Executive Support Systems and provide executives with information that allows them to have an overview of the entire business (Ward, 2006). Using an Executive Information System, those at the top level of management are made aware of what happens at the different levels of the business.
Other Types of Information Systems
Using Office Automation Systems, individuals can organize personal data and present information in a way that can easily be understood by the intended audience. They include word processing applications, spreadsheets and presentation packages (Ward, 2006). Communication systems improve the aspects of communication in the business while groupware systems let individuals work effectively in a group setup.
Information Systems for the Chosen Business
Despite the fact that it is a startup, the said business will do well by using some of the information systems explained in this paper. However, the systems may be implemented in phases as need arises. Initially, there will be a big need for a transaction processing system, office automation systems and communication systems. Systems for more complex operations will become necessary with time.
Benefit and Drawbacks
Generally, a business will enjoy numerous advantages by employing the use of information systems. There are, however, some drawbacks associated with the use of information systems.
First, an information system will make it possible for a business to manage complex operations that would otherwise be very challenging to deal with (Nel, 2007). The use of the identified information systems will also improve efficiency and production speed.
One of the major drawbacks associated with the use of information systems is the cost of acquisition. A business must be ready to invest heavily in the use of information systems. It is also important to note that maintenance is critical and this will increase costs even further. Without proper maintenance, quality will be compromised (Nel, 2007). The greatest fear of using technology is perhaps the fact that it can easily fail at the most critical time due to hardware or software failure.
Conclusion
Beyond doubt, the application of information systems will greatly improve the efficiency of a business. The business must, however, be ready to invest heavily in various aspects of using information systems. As an example, proper backups must be kept and a fall back is necessary.
References
Nel, W. (2007). Management for Engineers, Technologists and Scientists. Cape Town, South Africa: Juta and Company Ltd.
Ward, J. & Daniel, E. (2006). Benefits Management: Delivering Value From IS & IT Investments. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons.
