Introduction
The digital divide is a term used to refer to the gap between people, households, businesses, demographic areas, and countries with reference to their effective access to information and communication technologies (ICTs) and other digital forms of technology (OECD, 2001, pg. 4). It encompasses the disparity both in physical access and the resources required to effectively make use of the digital media and it reflects the various inequalities among and within countries. The ability of individuals and businesses to make effective use of the digital media around them differs significantly among countries and within countries with respect to their socio-economic status. Therefore, this parameter, together with others, can be used to measure the economic progress of a country. The term global digital divide is used to refer to the disparities in the access and effective use of digital media between countries.
Aim
The aim of the paper is to expound on the concept of the digital divide and discuss why it is important in today’s media-dependent society.
Discussion
The digital divide is perhaps one of the first concepts that come to mind when evaluating the social impact of ICTs on a country’s growth and development, one perceives that the use of digital media produces variations in the development opportunities of a people. The extent of this development will be heavily determined by the ability of individuals to access these technologies. Generally, the relationship between technology use and development is a direct one, for example, by not having internet access, a country is not able to impart IT knowledge to its citizens and hence cannot take advantage of the infinite amount of information available on the World Wide Web.
In contrast, richer countries have greater access to iCTs and the internet and can therefore reap the full benefits offered by these resources. These include e-commerce, e-business, e-democracy, and e-governance and these can help propel a nation’s economy and its citizens to higher levels and this places the poorer countries at a disadvantage in the global market.
Digital Divide Statistics
The UN’s specialized arm for telecommunications, the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) corroborates the concept mentioned above. Figures released by this agency reveal that the developing world has always lagged behind in terms of digital information access and use. This is illustrated below:
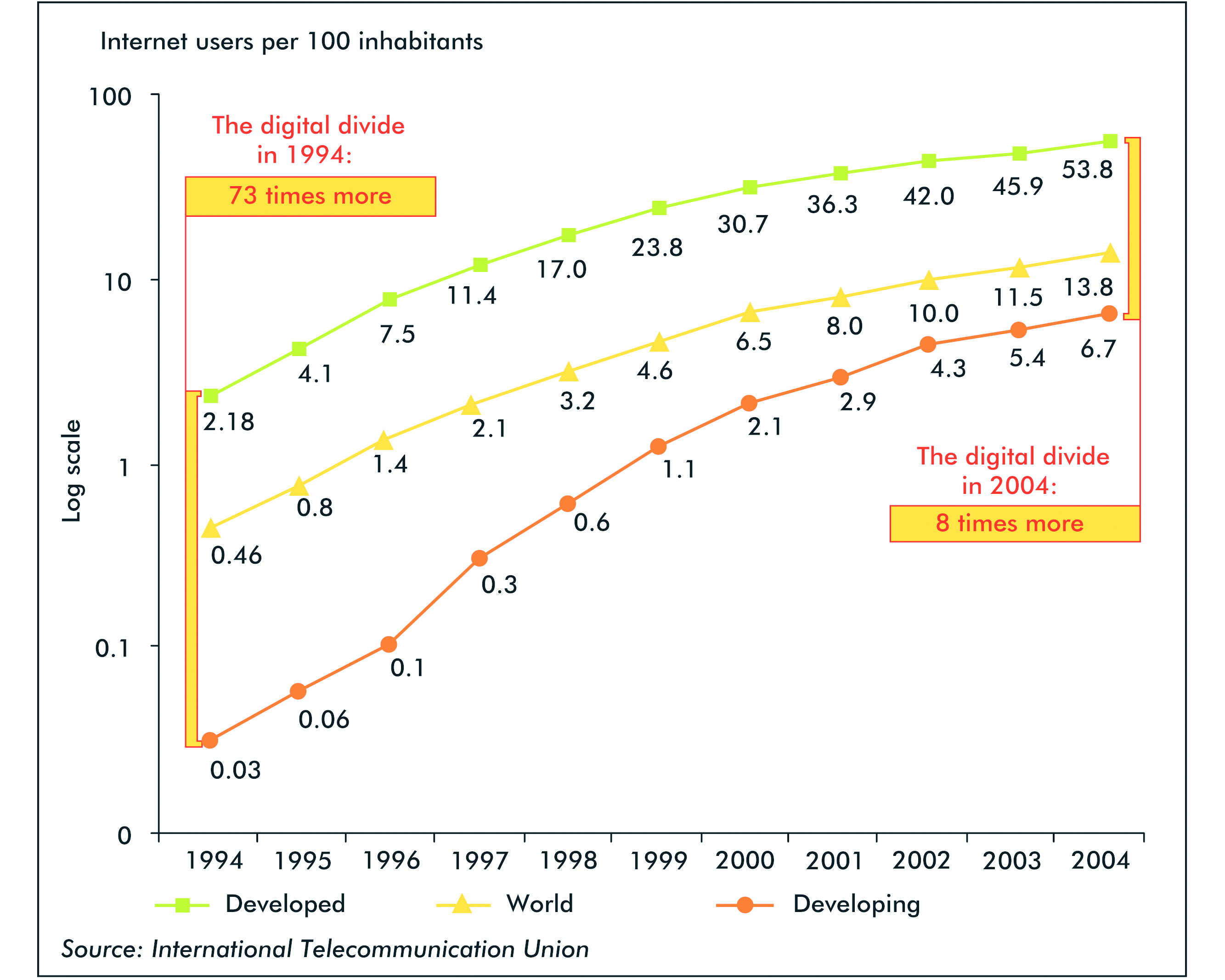
In 2004, the rate of internet penetration in developed countries was 8 times higher than that in developing countries.
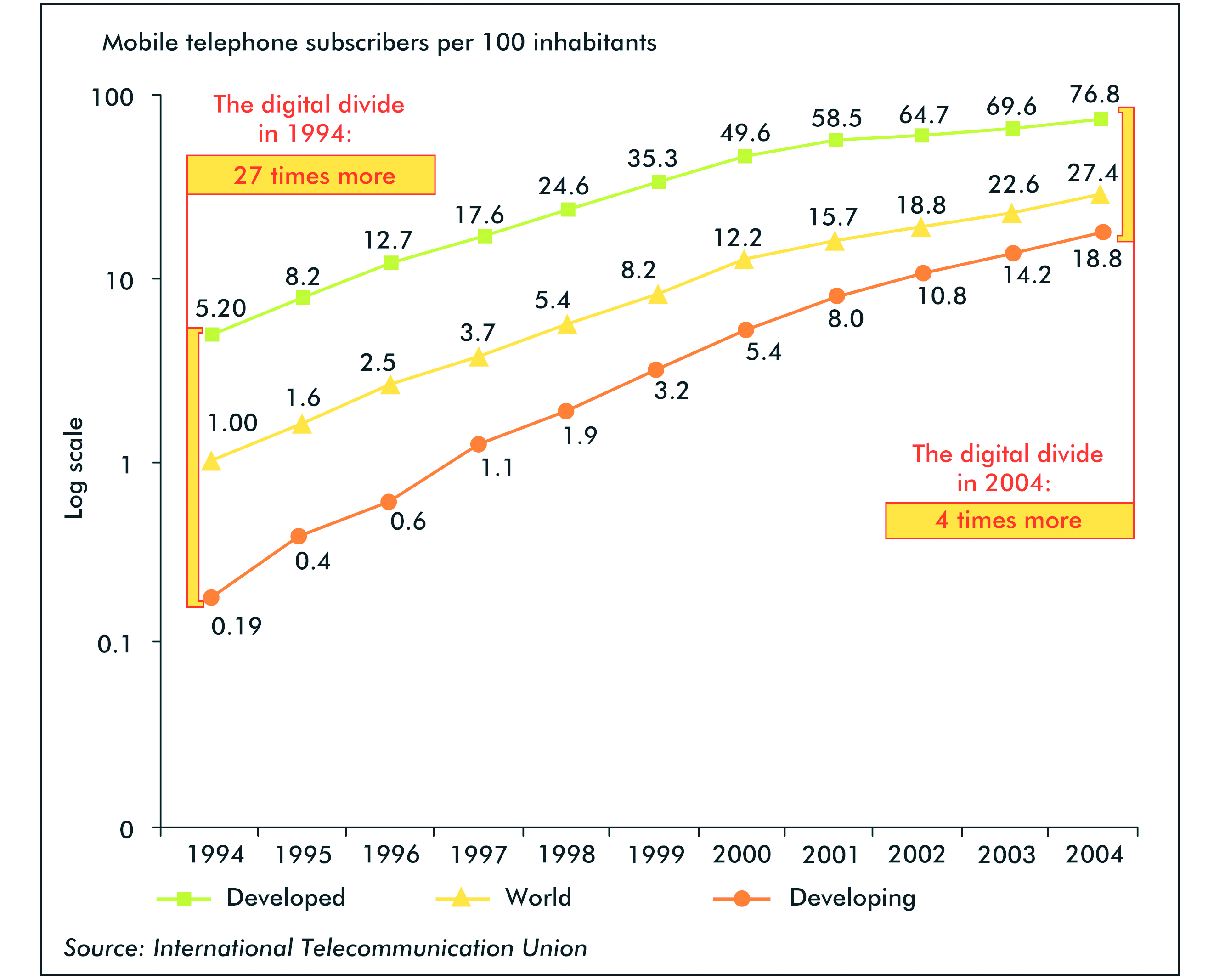
In 2004, mobile phone users in developed nations were four times higher than that of developing countries.
Further statistics from the ITU indicate that in 2004, less than 3% of the population in developing countries used the internet, a small figure in comparison to 50% among the G8 nations. The G8 nations, home to approximately 15% of the world’s population, have almost the same number of internet users as the rest of the world, the G8 nations also account for 34% of mobile users in the world (ITU, 2005, para. 4).
Conclusion
Besides creating economic disparities between the poor and rich, the digital divide has also created gaps between the young and old (Divided by Technology, n. d., para. 5). Only a third of the 35 million Americans over age 65 use the internet while almost 90% of persons aged between 18 to 40 years olds. This leaves the old out of touch with society and even those businesses that operate online. They also lack access to the vast amount of information available on the internet and for those that operate businesses, accessing the online market can become a challenge.
Reference List
Divided by Technology. (N. d). The Impact of the Global Digital Divide. Web.
ITU. (2005). The Digital Divide at a Glance. Web.
OECD. (2001). Understanding the Digital Divide. Paris: OECD Publications.
