What is an “endemic species”? Why is “endemism” used as a measure of habitat irreplaceability?
Endemic species are those species that inhabit a particular ecosystem only (Conservation International Web). Endemism becomes a measure of irreplaceability since endemic species cannot inhabit any other locality (Conservation International Web).
Why are vascular plants and vertebrate animals used to assess the degree of endemism of an area?
Vascular plants and vertebrate animals become objects to assess the degree of endemism in an area because researchers and conservationists have enough information concerning the vascular plants and vertebrate animals (Conservation International Web).
For a region to qualify as a Hotspot, what characteristics must it have?
A region qualifies as a hotspot if it hosts a minimum of 1,500 species of vascular plants and has suffered the loss of a minimum of 70 percent of its initial habitat (Conservation International Web).
What percentage of the Earth’s land surface is presently covered by the 25 Hotspots originally identified in 1999? How much of the original habitat has been lost from these regions?
The 25 hotspots originally identified in 1999 cover a paltry 1.4 percent of the world’s surface (Conservation International Web). 87.8 percent has been lost from the areas (Conservation International Web).
What percentage of terrestrial vertebrates and vascular plants are found in the 25 Hotspots?
The hotspots host 44 percent of the world’s plants and 35 percent of vascular plants (Conservation International Web)
What area is covered by the Wallacea Hotspot? Why is this Hotspot particularly important for birds? Wallacea is also home to which impressive reptile?
Wallacea covers 338,494 square kilometers (Conservation International Web). Wallacea hotspot is particularly significant for birds because it is the second-largest hotspot concerning bird endemism, regardless of its relatively small region (Conservation International Web). The hotspot hosts the biggest lizard in the world called the Komodo dragon (Conservation International Web).
The Southwest Australia Hotspot is renowned for its endemic plant diversity. How many endemic plant species are there? How many extinctions have been recorded? The endangered Southern Dibbler and the critically endangered Western Swamp Turtle are species from this region but how many other threatened vertebrate species are listed?
The southwest Australia hotspot has 2,948 endemic plant species (Conservation International Web). The area has recorded two extinctions (Conservation International Web). Other than the endangered Southern Dibbler and the critically endangered Western Swamp Turtle, there are ten more threatened vertebrates (Conservation International Web).
What are the activities that are threatening species like western chimpanzees and pygmy hippopotamus in Guinean hotspot?
Several activities that threaten Western Chimpanzees and pygmy hippopotamus in the Guinean forests of West Africa hotspot include timber harvesting, mining, hunting, and explosion in demographics (Conservation International Web).
Which Hotspot has the most recorded extinct species? Why? What makes these types of areas particularly vulnerable to extinction?
Madagascar and the Indian Ocean Islands have the highest number of extinct species. This is due to the reason that forty-five species are extinct (Conservation International Web). This is due to the natural isolation of these islands from the mainland. An increase in the human population is another cause (Conservation International Web).
Other than Australia, what are the other countries that are megadiverse? Provide a map as part of your answer and why are they considered so biologically important?
Other than Australia, the following countries are megadiverse: The Congo, Madagascar, South Africa, China, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Mexico, Peru, United States, and Venezuela (Australian Government Web).
The map below locates the seventeen-megadiverse countries.
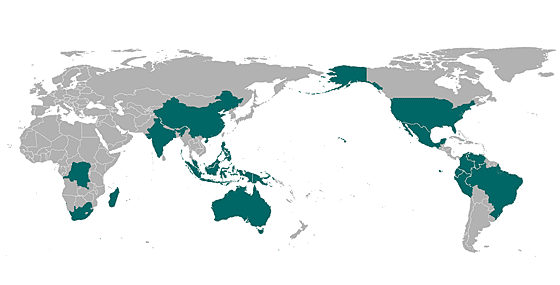
These areas are biologically significant because they support natural ecosystems and have a high diversity of locally endemic species.
National Hotspots – Australia
I have chosen North Kimberly in Western Australia. This hotspot suffers from excessive grazing, fire attacks, and continuous destruction of the landscape (Australian Government Web). Further, brutal cat and pigs populations are on the rise, while colonization by cane toads is a potential threat (Australian Government Web).
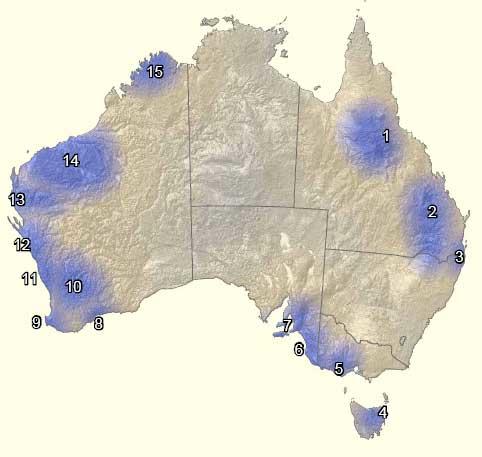
The hotspots are along the seacoast because this is where endemic species inhabit bearing in mind that Australia is an Island.
References List
Australian Government. Biodiversity Hotspots, Web.
Conservation International. Hotspots, Web.
