Introduction
A project can be defined as a time constrained endeavor with well-defined starting and end points. A project normally is constrained by deliverables and funding, and is normally undertaken to meet some specific goals and objectives.Project management can be defined as that field concerned with the organizing, planning, leading, managing and controlling of resources in order to achieve a specific goal. The process of project management can be a daunting process fraught with disappointments. Hence, people mandated with the responsibility of managing projects are normally faced with intricate decisions that will see the proper completion of a project (Lock, 2007).
This essay is going to critically evaluate a real project that is being undertaken. The essay will also examine the various methodologies, and strategies towards proper project management.
The license application mitigation program (LAMP) project
The license application mitigation program was initiated in 1990 by the state of Washington. The main goal of the project was to automate the process of state vehicle licensing renewal, and registration of vehicles (Laudon & Laudon, 2000). The project was estimated to run for a period of five years, which meant that, the projected was expected to end in the year 1995. The project was projected to cost $16 million over the entire time frame it was to last. However, this was not the case as the real budget of the project increased from time to time (Laudon & Laudon, 2000).
The following table indicates a breakdown of how the budget for the project increased.
A project scope will define what must be done in order to produce the projected and expected results from the project. The above project lacked a defined scope since it was not broken into smaller parts that could help in defining the project scope (Laudon & Laudon, 2000). There were a lot of cocktail activities that were to be undertaken ranging from legislation amendments to hardware, and software installations. This even led to the managers of the project changing some of the project requirements along the way.
The LAMP project was faced with a number of constraints that led to the cancellation of the project in 1997. They include the following; poor project management, lack of a defined scope, and a split between the project developers(Laudon & Laudon, 2000).
Poor project management
The entire project was poorly managed, a factor that was attributed to the cocktail of managers who were mandated with the task of managing the project. This led to the problem of administrative meddling because; most of the project managers were political appointees, and a mix of elected officials. These project managers were inexperienced in project management, and most of them did not consider the Lamp project as a priority. Also, the project managers overlooked the signs of the project failure which was evident in the first two years since the inception of the project (Laudon & Laudon, 2000). Most managers did not want to hear that the project was a failure.
A split between the project developers
There was a problem between the in-house and private developers of the project. This led to lack of communication and coordination between the private developers and the in-house developers(Laudon & Laudon, 2000).
Lack of a defined scope
Last but not least, the project lacked a defined scope. The project was a big idea which was associated with very few go-between deliverables. The project managers did not break the project into measurable and smaller chunks(Laudon & Laudon, 2000). This led to most of the project requirements being changed over, and over again. This is evident in the events that followed after the departure of Lindamood. After Lindamood left, the project legislators were forced to pass new registration, and legislative laws which adversely affected the project scope leading to more project delays(Laudon & Laudon, 2000).
Three-sphere model of systems management
The three sphere of project management is an important tool towards managing information technology projects. The three main sphere of project management include the following sphere; business, organization and technology. For proper project management, there should be a high level interaction between the three spheres (Newell & Grashina, 2003).
Business costs. A project manager should calculate the overall costs the project is going to undertake. The business costs will include both the monetary expenses that will be involved in the implementation of the project. Also, the business costs will include the overall monetary benefit the project is going to bring to a business. For example, in the purchase of laptops for hospital, the business costs will include the total value for both the hardware, and he software (Grun, 2004).
Technology. Another aspect of project management is the technology sphere. Project managers should select the relevant technologies that are effective and efficient. Such technologies should reduce the overall costs for managing the projects. There are various changes that are being experienced in the information technology field; hence, relevant technologies should be adopted (Reschke et al, 1990).
For example, in creating a database management system for a college, then, a project manager should adopt the relevant technologies. The adopted technologies should be in apposition to provide more functional data management abilities like data mining. For instance, the project manager should consider adopting sophisticated data management applications like oracle databases.
Resources. Resources are those materials that aid in the implementation of the project. Resources are an important ingredient in the process of project management. In order to have a viable project, then, project managers should select project resources more carefully, and with due diligence it deserves. Relevant technologies required to complete the project should be identified, and assigned to the relevant people (Grun, 2004). Resource allocation should also involve the process of training the resource users on how to effectively use the resources. This will lead to a reduction in the overall cost of the project because of the optimal usage of resources (Newell & Grashina, 2003).
A good example of an information technology project that was conducted is the implementation of an automated staff login system at the University of California. The business aspect of the project was to increase employee performance hence leading to a high customer service delivery. The project was intended to ensure that employees of the institution are always present at workplace and performing the duties assigned to them in due time. This was to eventually increase employee productivity in the institution, and also increase the level of customer satisfaction(Grun, 2004).
The technological issues that were witnessed included the adoption of a relevant technology that will not only monitor the login system but also manage the leave status of employees. The system was also required to help manage the leave status of employees and also allow employees apply for leave online. Such a platform also required the presence of an intranet that will allow employees to login and apply for leave forms as well as check their leave status.
Also, the other technological issue that was experienced was the issue of employee identification. Employees were to be uniquely identified by the system without any errors. The system was supposed to identify the employees given a unique identification. This could only be achieved by using a bio-metric application that identified employees depending on their finger prints.
The major organization issue that was identified is the issue of employee resistance. Most employees of the institution felt that they are being monitored which deprived them the freedom they required. They noted that, they required some degree of freedom, and they could as well be more productive without the system. Also, the employees noted that, they are driven by a sense of maturity, and they did not require the system in order to perform their duties on a full time basis(Newell & Grashina, 2003).
PRINCE2 Methodology
PRINCE (Projects in Controlled Environments) 2 is a well-structured approach to managing projects. The approach was developed in 1996 which integrated the IBM’s managing the implementation of the total project (MITP) and the PROMPT method to project management. The PRINCE 2 method has well and clearly defined framework that assists project managers to effectively manage projects. The system provides a guideline on how managers should guide, and manage people and activities in a project (Office of Government commerce, 2009).
The system also provide protocols on how to supervise and design a project, and the relevant measures that can be taken in order to adjust the project in case it is deviating from the expected course. In the PRINCE 2 method of project management, the entire project is sub-divided into smaller units with inputs, and outputs (Great Britain, 1997).
Project managers prefer the PRINCE 2 method because of a number of reasons. Firstly, the method allows easier project management because the entire project is subdivided into smaller manageable units. This allows for close monitoring since, the project is undertaken under an organized and controlled manner(Office of Government commerce, 2009).
Secondly, most managers prefer the PRINCE 2 method because it reduces the complexity associated with a project. The project describes, and distinguishes the various management responsibilities which are adapted to suit the complexity of the entire project(Great Britain, 1997).
The following diagram indicates the PRINCE 2 process model.
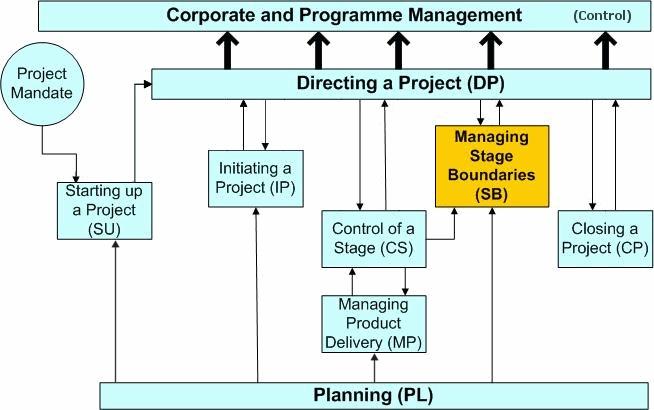
PRINCE 2 method involves the following steps; stating a project, initiating a product, directing a project, controlling a project, managing stage boundaries, managing product delivery, and closing a project(Great Britain, 1997).
There are various organizations that have effectively used the PRINCE 2 methodology of project management. The UK government has in the recent past constantly used the method in its projects management endeavors(Great Britain, 1997).
Conclusion
In conclusion, the process of project management is an intricate and daunting task that requires careful and efficient management. Project managers should take the relevant, measuresthat will ensure that, the project is undertaken within the time frame as well as the budget for the project. Also, project managers should ensure a careful selection of a project management methodology that will ensure that the project is undertaken within the specified scope.
Reference List
Great Britain. (1997). PRINCE 2: An outline. London: HMSO.
Grun, O. (2004). Taming giant projects: Management of multi-organization Enterprises: With 31 tables. Berlin: Springer.
Laudon, K. C & Laudon, J. P. (2000). Management information systems: Organization and Technology in the networked enterprise. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Lock, D. (2007). Project management. Burlington, VT: Ashgate.
Newell, M. W & Grashina, M. N. (2003). The project management question and Answer Book. New York: AMACOM,American Management Association.
Office of Government Commerce (OGC). (2009). Managing successful projects with PRINCE2. London: TSO (The Stationary Office).
Reschke, H & Schelle, H & Gutsch, R. W. (1990). Dimensions of project Management: Fundamentals, techniques, organization, applications. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
