Outline
This study deals with the tourism strategy adopted by Jordan as a part of developing the tourism industry of the country. In this study the effectiveness of the strategy in terms of tourism theories are discussed and analysed. In order to identify the potential strength and weakness of the tourism industry in the country is analysed through SWOT analysis. The national tourism strategy adopted by the country are analysed with these factors. A c-pest analysis and resource analysis is also conducted for identifying the potential competitiveness of the industry in meeting the motivational requirements as per the theory of travel motivation. The discussion revealed that the national tourism strategy has potential strength to motivate the travellers and it will contribute to the development of the tourism industry in the country.
Tourism strategy of Jordan
Brief synopsis of the Jordan Tourism Development Strategy
Tourism is an important contributor of national revenue of Jordan by way of tax as well as foreign exchange earnings. It is the fastest growing industry in the country. The joint effort of government and industry leaders, the National Tourism Strategy2004-2010 is an important step which stimulates the growth of the sector. Private investors, public sector representatives, and NGOs are take parted in the implementation of the strategy for creating employment and entrepreneurial opportunity beneficial for the well being economy as well as society. The strategy is concentrating on the following goals; “ Strengthening the tourism marketing, supporting product development, developing human resources, providing an effective institutional and regulatory framework.” (Jordan’s National Tourism Strategy 2004 -2010, 2009).
Jordan tourism is showing higher growth rate over the recent years. In the year 2008 the industry recorded 27% growth compared to last year, which is the result of the national tourism strategy adopted by the country. Positive growth arte is shown, in the field of inbound traffic and package tours in the country. “Jordan recorded 27% increase in 2008 amid the global economic turmoil, largely due to the proper implementation of tourism strategies in the country. Jordan, tourism industry of Jordan grew massive 27% in 2008 as compared to previous year, as reported by MENAFN.” (Jordan Tourism Industry – Good Times Over, Gearing Up for 2009, 2009).
Jordan adopted tourism centric strategy which is capable of ensuring healthy growth of the economy. Good infrastructural environment, attractive tour packages of the national tour operators and government support at all levels are the major factors that affect the positive growth in the tourism sector of the country. The main principle of Jordan’s national tourism policy is to provide maximum benefit to the national economy as well as local community. Through the successful implementation of the strategy it is expecting that the country will gain increased economic growth and foreign exchange earnings. “The Kingdom unveiled its long-awaited National Tourism Strategy with a well-defined plan aimed at reversing years of under-performance and lagging development within the competitive global tourism market.” (Jordan: National Tourism Strategy Unveiled, 2008).
The rules and main elements of the strategy are formulated by the joint decision of government and industry leaders. Tourism opportunities in the country are identified by the government and policies are formulated to exploit these opportunities. Value chain concept is adopted by the country which is focusing on providing improved tourist experience to the visitors. The taxes collected from tourism industry are reinvested, tourism marketing and product development. “Jordan’s National Tourism Strategy, 2004 -2010, developed with American aid and technical support, and represents an effort to better address the complexity of global tourism markets by identifying the diverse niche segments to which Jordan should adapt its tourism development and marketing efforts.” (Hazbun, 2008).
The national tourism strategy of Jordan is aimed at doubling the tourism economy by the year 2010. It is through significant investment for the development of niche markets, enhancing the experience of travellers, stimulating the international marketing, with the support of advanced infrastructure facilities and regulatory environment. An integrated value chain approach is adopted by the project implementation and the involvements of government as well as private investors are assured.
The strategy has the following objectives
- Increasing the revenue from the industry to a level of US$ 1.84 billion.
- Increase the job opportunities related to the industry of over 51000 jobs.
- Increase the tax yield from the industry at a rate of more than US$ 637 million.
The strategy is objected to attain the targeted growth through focusing the areas such as cultural heritage tourism, religious tourism, eco tourism, medical tourism, adventure tourism, business tourism, cruising tourism etc. (Jordan National Tourism Strategy 2004- 2010) (Provided by customer)
Sustainable tourism is the adopted policy of Jordan tourism industry. The conservation of world heritages sites in the country is the core of their tourism development policy. For this purpose, they come in co operation with US and thus US AID Jordan tourism development project is started in the country. For the promotion of sustainable tourism, the collaboration of private sector and civil society is also ensured by the country. Petra is the primary world heritage site in the country. Responsible tourism is also adopted policy of Jordan tourism development. For this historical treasures occupied by the country are conserved as a part of the tourism development. “The Jordanian case presents its tourism strategy as focused on more tourists, higher spending, and longer stays. The plan aims at making Jordan one of the top tourist destinations, yet there is no clear mechanism by which the Jordanian Tourism Board appears to be achieving this goal.” (Fawzy, 2002, p. 241).
Tourism theories
Travel and tourism theories are mostly based on travel motivation. The basic factors that influence the travelling decisions are tourist need satisfaction, customer satisfaction and destination loyalty. Tourist motivation factors have higher influence on the tourist behaviour of travellers with regard to their destination choice, needs, goals and preferences. In case of ecotourism, social psychological desire to break out from the habitual ordinary life is the primary push factor. The major pull factors which force travellers to take travel decisions are destination attributes such as natural attractions such as wild life and immaculate environment. (Kim Lian Chan, & Baum, 2009).
As per the theory of Iso- Ahola interpersonal escape and interpersonal seeking motivate tourism and recreation among the individuals. In case of personal seeking and personal escape dimensions, tourism experiences have great role in motivation. Sporting events, beaches, amusement parks, and natural parks improves the motivational levels of tourism and recreational activities at a greater extend. (Snepenger, etal, 2006).
Tourism motivation in holiday trips is the desire to travel for satisfying the internal needs and wants. Incentive tourism is a motivational tool among the employees as well as other organizational personnel. Most of the weekend travel decisions are related to the intention to take rest and spend the weekend for relaxation. Travel behaviour among individuals can be described as a function of quantifiable aspects such as socio-demographic characteristics and physical characteristics of the region. Most of the travelling decisions are situational in nature.
Travel behaviour of individuals is influenced by individual personality, attitudes and perceptions. Attitude of travellers have influence on beliefs and behaviour in travel decision such as the frequency of use. Novelty seeking is the prime motivating factor that affects the travelling of most of the individuals. The positive and negative feed back from the travel affect their future decision to travel a particular destination.
The motivational factors have a key role in the tourist decision making behaviour. In the motivational factors push and pull concept was introduced by Crompton and Chon in 1979. Push factors affect the desire for travel where as pull factors affect the actual destination choice. In the concept of Crompton 1979, there are nine motive factors influencing the leisure travellers. Seven of them are socio psychological factors and two are cultural motives. Push factors are internal factors whereas pull factors are external The seven push factors include, making a change the routine life environment, meeting self needs, relaxation, establishing social relationships, prestige and social interaction. Novelty and education are the pull factors. According to Iso-Ahola, 1980, there are mainly two motivational factors in tourist behaviour. The first feature is approach, focusing on recreational opportunities for intrinsic rewards, and the second feature is avoidance which is escaped oriented. The increasing trend of shorter holiday breaks is a signal of escape dimension among the tourists behaviour.
The study by Teare ( 1994) on peoples motives for selecting hotel leisure breaks in the UK states that there are six factors such as attending a pre arranged event, as a break from personal commitments, as well as employment pressures, to fulfil the desire of relaxation or vast a particular destination and to exploit the seasonal benefits of short breaks. The personal motivation factor may differ as per individual behaviour. (Dunne, Buckley, & Flanagan, (n.d)).
Analysis of tourism strategy of Jordan with relate to tourism theories
The SWOT Analysis of Jordan Tourism Industry
The SWOT Analysis conducted for analysing the strength and weakness of the Jordan tourism Industry. And also, the analysis of the opportunities or future prospects and the possible threats or obstacles that may arise during the development of the industry is done in this part.
Strengths
Tourism is one of the major sources of national income for of Jordan. Jordan is characterised by wide range of rich, historical, cultural and religious sites. The tourism destination in the country is attracting ever growing number of visitors. Tourism is the second largest industry in the country and it contributes for about a tenth of the country’s GDP. It is one of the famous tourist countries in the world. The country has some unique tourist attracting places such as “Petra Nabatean City in rocks (culture), Dead Sea (health), Baptism Site by the Jordan River (religion), and Wadi Rum Desert (eco-tourism).” (Taisir Taji, (n.d), p.1)
It will be capable of attracting the travellers by providing unique experience on travel.
Jordan has the ability to and resources to attract more tourists than other competing countries liken Saudi Arabia, Egypt…etc. “Camel ride in Wadi Rom, wonderful nights in Bedouins tents in the desert, birds watching in natural reserves are only few examples of the diversity one can encounter while having a trip in Jordan.” (Tourism, (n.d)).
Weaknesses
The present financial recession will affect the growth of the tourism sector of the country badly. Regional political instability is a serious challenges faced by the industry. Attacks of terrorist are restricting the growth of the tourism sector. There is no proper mechanism for the disposal of the wastages in beaches and other tourist places. This may cause problems to the natural environment of the country.” Solid waste is considered a particular problem in Jordan. The beaches and near shore reef and sea grass areas of Jordan’s Gulf of Aqaba are heavily polluted by discarded plastic and other refuse materials.” (Threats, 1997).
This is considered as one of the serious weakness of the tourism industry. There is an acute shortage of the skilled professional in the tourism field. This may results in decreasing the number of tourists who are travelling to the country. “The industry is suffering from a shortage of skills specific to hospitality and tourism including: communication, customer care and quality, supervisory management skills, marketing and sales techniques, and professional skills training in operational areas.” (Jordan’s Competitive Report 2007, 2007, p.24).
As per the motivation theory, this will restrict the travel behaviour of individuals badly.
Opportunities
There are endless opportunities for the Jordan for improving the tourism industry. “When it comes to tourism, Jordan is as rich in untapped potential as it is in historical sites, hence the considerable opportunity for developing more destinations that act as tourist magnets within the country.” (Developing Competitive Tourism Destinations – A Cluster Approach, 2006). So, if the concerned authorities take positive and supportive action for the improvement of the tourism industry, the country can be one of the top tourist countries in the world. Another important point to be noted here is that, Petra in Jordan is one among the new Seven Wonders of the World. This can be taken as a golden opportunity for the development of tourism industry by way of attracting tourists. “With the growing fame of the rose-red city of Petra in light of its selection as one of the New 7 Wonders of the World, both the government and private sector will have to work together to preserve important sources of revenue, history and pride.” (Luck, 2009).
Threats
The threat and attack from the terrorists act as obstacle in the development of the tourism industry of the country. If any tourist is killed by the terrorist attack, it may cause to decrease the number of tourists coming to the country
“Jordan ahs benefited from the relative calm along its boarder with Israel over the past few years, but like Israel and Egypt, it has been hurt by the political conflicts and boarder changes in the area. During 1991, the Gulf war reduced its tourism to almost zero.” (Hudman & Jackson 2002, p. 354).
Another threat the country’s tourism facing is that the threat from the thieves. The tourists some times become the victims of the robbery. If any tourist gets such experience he will be telling to other people about his experience in Jordan. So this may cause to avoid Jordan from the list of places to be travelled by the tourists from different part of the world as per the tourism motivation theory.
C- PEST analysis
Competitive environment
The traditional tourism attractions in the country are of declining in nature. To improve the competitiveness of the tourism products in the country, innovative developmental efforts capable of improving the experience of visitors are carried out by the tourism development board. Regional governments are also actively participated in the tourism development activities. Various kinds of investment such as capital investment, product development & innovation, marketing services and human resources etc are ensuring the success of the strategy. The country will gain sustainable tourism development through the sustainable tourism policies. Jordan tourism development is made on the basis of targeting the niche tourism market. Biblical and archaeological sites in the country are well protected and preserved. “Attacks on tourists and tourism resorts in the region over the past few years have raised new concerns. Turkey, Egypt and Jordan all suffered terrorist attacks in 2005. The threat and impact of such attacks is considered one of the most pressing challenges facing the industry.” (Dajani, 2006).
Political environment
The government is committed to the development of the industry as they understood the potential of the sector in the overall economic development of the nation. Regional and international image of the country is also attractive in the tourism industry. Efforts for effective utilisation of available tourism products in the country are also adopted by the government. The services offered to tourists are also of great standard. The political instability in the Middle East region is a major threat that negatively affects the tourism development of the country. Increasing terrorist attacks is also challenging to the Jordan tourism development.
“In Jordan, the government seems to be taking the guiding role that appears so necessary for the smooth growth and development of the tourism and appears to be addressing some of its negative impacts.” (Joffe et al, 2002, p. 325).
Economic environment
The macro economic environment of the country is of stable in nature. Greater public sector participation is allowed in major segments of the economy including tourism. The monetary policy of the government is adequate for overcoming the financial barriers. Major competency of the country is in the field of health, education, and the efficient and qualified work force. “GDP has been growing at a sustained rate of 5-7% in the last 5 years and touched 7.7% in 2005, while the GDP per capita has grown from USD $1,700 in 2001 to over USD $2,400 in 2006.”
(Assessing the Foundations of Jordan’s prosperity, (n.d), p.4). In the construction industry, service sector infrastructure development is of greater importance. And it provides greater importance to the tourism infrastructure development. (Jordan news report, 2008).
Sociological environment
The poverty rate in the country is of declining in nature. Educational infrastructure is greatly developed in the country and thus 100% literacy is achieved for both men and women. The health statuses of the citizens are also improved. These achievements helped the country to gain better position in the ranking of UNDP HD index. It will provide better image among the global travellers and will motivate them.
Technological environment
Technological environment of the country is supportive for tourism development. In order to provide greater accessibility to the important tourism destination in the country, different ways of transportation is arranged. For enhancing the air transportation facility open sky policy is adopted by the country. “The open skies policy allows foreign airlines to operate charter and regular flights into countries without necessarily being bound by reciprocal agreements.” (First Jordan multilingual business and tourism portal, 2004).
Resource analysis
Jordan occupies many peculiar destination characteristics which provide potential growth opportunity for the sector. Prominent tourism attraction in the country includes Petra, Wadi Rum and the Dead Sea. The potential strength of the destination is not fully exploited for the tourism development. It can see that the performance of tourism sector in the country is performing below its potential level. In order to achieve successful growth in the sector, investment of public as well as private fund is necessary with effective strategy.
Eco- tourism opportunities
Eco tourism is considered as a tool for conservation. Jordan has greater potential in eco tourism and medical tourism. The regional and rural development will become possible through the strategy and the country will get a stronger position in the competitive world tourism market. The destination features of the county characterised by unique nature beauty, and historic inheritance is ensuring tremendous growth opportunities in the eco tourism sector. Jordan River is a major attraction in the country which is a holy river also for the Christianity. During summer vacation the arrival of tourists from the GCC countries to the Jordan is of increasing annually. There exist nine different reserves in the country occupying distinct eco system.
Religious tourism
In Jordan there exists greater potential for religious tourism as it is the birth place of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. As the sacred place for these religious groups, Jordan has greater attraction among religious tourists. The tourism development project in the country is fusing on providing an improved spiritual experience to the tourists. In the global tourism market, religious tourism is an important sector and in Jordan a very strong market is of existing. Ancient sacred sites in the country are attracting so many visitors annually. Lot’s museum in the country is a greater contribution for the development and expansion of this unique sector.
As a part of the project investment for an amount of $ 1.76 million are employed in the development of the religious heritage sites. As the burial site of Moses, Mt. Nebo has attraction among the Judaists travellers. Archaeological and religious tourism is greatly promoted by the Tourism Board through attractive packages. The trend in the religious tourism is of continuing in nature even in the occasion of increasing regional conflicts in the Middle East.
Cultural heritage tourism
The heritage sites such as Petra, Wadi Rum, and Dead Sea are considered as invaluable assets for tourism industry of the country. There exists greater possibility of heritage tourism related to these sites. The effective utilisation of these unique resources will be of greater advantage to the industry growth. Ancient Byzantine temples in Petra are of attractive in nature. The Tomb of prophet Haroon in Petra and as such holy burial sites in the country is attracting large number of Muslim tourists annually. “The promotion of these sites has shown immediate dividends. In 2005 more than 75,000 tourists visited the baptism site alone—25 percent more than in 2004—generating JD350, 000 ($493,990) in revenues.” (First Jordan multilingual business and tourism portal, 2006).
Medical tourism
The development of medical tourism in the country is targeting Europe and North America. As per the findings of World Bank, Jordan is the number one health tourism destination in the Arab region. The cost effective quality health services available in the country is supportive for growth of the health tourism sector. From the sector, the country attained $ I billion in 2007. “According to PHA statistics, some 250,000 foreign patients from more than 80 countries were treated in Jordan last year.” In the Gulf region medical tourism is a growing field. (Jordan news report, 2008). The services of highly specialised doctors supported with world class health facilities and common language are the major competitive advantages of Jordan health tourism.
Adventure tourism
Jordan has greater potential in the field of adventure tourism. Adventure travel is of greater acceptance among the customer base. Through the combination facilities such as physical activity, experience to the natural environment, by collaborating with local cultures. Sustainable tourism promotion activities are carried out in this sector. Economic, environmental and social benefits of the sector are identified. Cycling, canoeing, swimming etc have facility in the country. For learning about the features of Middle East Jordan is a suited location. “Adventure travel, with its focus on more in-depth explorations offers people a new, authentic and largely untapped way to experience the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan.” (New adventure travel partnership consults on Jordan’s developing tourism industry, 2009).
Archaeological tourism
It is also strong in the region as it by combining the features of wild life and archaeological tourism. Dana nature reserve is a best example of the combination of archaeology with wild life tourism. Petra in Jordan is selected as one of the new seven wonders improved its tourism value. The country is occupying resources for developing sports tourism as a niche market.
Infrastructural facilities in the country
The arrival and departure of major share of tourists in the country is mainly by way of land. There is also booming trend in the air transportation in the country. The increase of business tourism in the country stimulates the air transportation. Government adopted steps to build new terminal at the major international airport capable of increasing the present capacity by almost three times. The country is also takes step to strengthen its railway networks. For better serving the local destinations, and eventually expand to regional destinations. These will improve the accessibility of the destination and enhance tourist arrivals. (Travel and tourism in Jordan, 2009).
Human resources
The tourism development in the country needs adequate human resource in the hospitality field. Jordan government is taking adequate steps for ensuring availability of human resource in the tourism sector. “The government of Jordan is committed to allocating four percent of national tourism receipts for international marketing, product development, and human resources development through 2010. These contributions will more than double the current level of tourism investment.” (Jordan National Tourism Strategy: 2004 – 2010, 2006).
In the academic studies, tourism and hospitality management is included as a major subject. In the universities, training in hospitality is provided to the youngsters as a part of the academic study. It ensures availability of well trained staff in the sector.
Tour operators and hotels in the country are playing active role in the tourism development. In order to maximise the benefits from the industry they play crucial role. The Jordan tourism development project is focusing on informing the industry members for educating responsible practises to the tourists while they are on heritage site visit. The marketing facility for locally made products and services are also arranged near such sites. E-marketing is adopted by the JTB for promotional measures supportive for Jordan Tourism development project.
Skilled hospitality workers are better developed in these institutions. Siyaha is a project of the government to strengthen the skills of the individuals capable of meeting the requirements in the growing national tourism industry. It is intended to improve the service quality in the industry with improve job opportunities. “Siyaha is also providing a range of support to the sector as a whole, including improving tourism-related business associations, developing new quality assurance standards, launching an awareness campaign about the benefits of tourism to the country, and strengthening the tourism sector’s research capacity.” (Component 3- Human resources and sector support, 2009).
Jordan tourism strategy is aiming to increase the revenue growth from the industry by targeting to the smaller and higher margin market segments. Upscale service in the niche market destination is provided for stimulating the growth of the industry. Due to the constrained natural resources, Jordan has limited possibility for mass tourism.
Conclusion
The sustainable growth and development of the tourism sector in Jordan is greatly related to the conservation and guard of the cultural and historic sites in the country. As per the theory of motivation, uniqueness in the travel experience will act as push factors for the travel decision. In this concept the national tourism strategy focused on sustainable tourism will be effective for sustained growth of the sector with widely attracting the travellers. The tourism industry is requiring continuous changing policies and strategies for meeting the changing needs, tastes of the visitors. Adequate steps taken by the government for improving the tourism image will be effective for influencing the travel decisions of customers.
The multifaceted operational strategy with the collaboration of private and public sector should be of greater effective for attracting the travellers. The strategy is acting as a guide for attaining sustainable growth in the tourism industry. It aims to achieve the goals through a competitive value chain approach. There will be balance in between the growing tourism demand as well as the nature conservation.
Appendices
Statistical data on Jordan Tourism
“Population: 4.6 million
Currency: Jordanian dinar
Total Arrivals: (2001) 1,477,697
Total Receipts: $722 million+ (2000)
GDP: $15.5 billion
Inflation Rate: 4 %
Unemployment Rate: 15%
Airports: Amman international airport
Ports and Harbors: Aqaba
Exchange Rate: JD1 = US$0.090 as at 2002 “
(Source: Jordan.(tourist information)(Statistical Data Included).
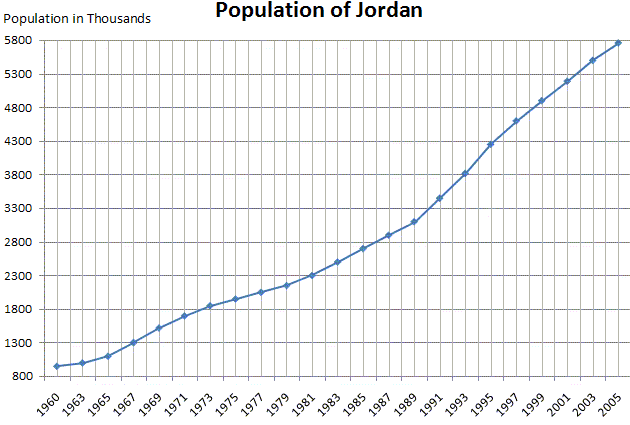
Graph showing population growth in Jordan from 1960 to 2005:
Reference
Assessing the Foundations of Jordan’s prosperity: Macro economic performance. (n.d). 4. Web.
Coping with terror threat to tourism. (2006). BBC. Web.
Component 3- Human Resources and sector support. (2009). USAID from the American People: JORDAN Tourism Development Project. Web.
Dajani, Dalya. (2006). Summit to address challenges facing industry. Jordan Times. Web.
Developing Competitive Tourism Destinations – A Cluster Approach. (2006). Siyaha. Web.
Dunne Gerard., Buckley, Joan., & Flanagan, Sheila. (n.d). City Break Travel Motivation- The case of Dublin. Web.
Fawzy, Samiha. (2002). Globalization and firm competitiveness in the middle east and North Africa region. World Bank, p. 241. Web.
First Jordan multilingual business and tourism portal: Niche tourism. (2006). 1st Jordan. Web.
Hazbun, Waleed. (2008). Beaches, Ruins, Resorts. U of Minnesota Press. P. 201. Web.
Hudman, Lloyd E., & Jackson Richard S. (2002). Geography of travel and tourism. Cengage Learning, p. 354. Web.
Joffe, George H et al., (2002). Jordan in transition. Palgrave Macmillan. P. 325. Web.
First Jordan multilingual business and tourism portal: Influx of tourists emphasize Jordan’s diversified tourism. (2004). 1st Jordan. Web.
Jordan’s National Tourism Strategy 2004 -2010. (2009). USAID: From the American People: JORDAN Tourism Development Project. Web.
Jordan Tourism Industry – Good Times Over, Gearing Up for 2009. (2009). RNCOS Industry Research Solution. Web.
Jordan: National Tourism Strategy Unveiled: description. (2008). Goliath. Web.
Jordan’s treasures become tourist destination challenge: Results. (2006). USAID From the American People. Web.
Jordan’s Competitive Report 2007: Tourism: Key Industry Facts. (2007). Jordan National Competitive Team. 24. Web.
Jordan news report. (2008). Arab-Hellenic Chamber. Web.
Jordan news report: Jordan going places. (2008). Arab-Hellenic Chamber. Web.
Jordan National Tourism Strategy: 2004 – 2010: Goal. (2006). Embassy of the Hashemite Kingdome of Jordan in Canberra. Web.
Kim Lian Chan, Jennifer., & Baum, Tom. (2009). Motivation Factors of Ecotourists in Ecolodge Accommodation: The Push and Pull Factors. Informa World. Web.
Luck, Taylor. (2009). ‘Balance between responsible tourism and preservation required for heritage sites’. The Jordan Times. Web.
New adventure travel partnership consults on Jordan’s developing tourism industry. (2009). Terracurve. Web.
Snepenger, David., etal. (2006). Modeling Iso-Ahola’s Motivation Theory in the Tourism Context. Journal of Travel Research, 45(2), 140-149. Sage Journals Online. Web.
Taisir Taji, Elina. (n.d). Marketing strategies for tourism recovery in Jordan (emphasis on niche market): Abstract. Web.
Tourism. (n.d). 1st Jordan. Web.
Threats: Sewage and solid waste: Jordan. (1997). UNEP. Web.
Travel and tourism in Jordan. (2009). Euromonitor International. Web.
World heritage alliance meets with tourism sector in Jordan. (2009). USAID From the American People: JORDAN Tourism Development Project. Web.
