Introduction
Climate change has become a matter of increased concern. The Earth has experienced a 2-degree rise in global temperature since the pre-industrial era (Lindsay and Dahlman, 2020). Therefore, it is crucial to address the problem of climate change as soon as possible to mitigate its negative effects. This presentation aims at explaining climate science in simple term to increase awareness about environmental problems. First, we are going to discuss the carbon cycle and its importance. Second, we will discuss the climate system and how it is affected by human activity. Third, we are going to explain climate change, its implications, and challenges in addressing the problem. Finally, We will describe possible strategies for addressing climate change that everyone can use.
Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle is a natural process of reusing the atoms of carbon for a wide variety of purposes. Carbon is a vital element for living beings, as it is an essential part of nucleotides, amino acids, sugars, and lipids (Biology dictionary, 2019). The carbon cycle begins in the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2). The gas is released into the atmosphere as a result of animals’ and plants’ breathing process, burning, or the activity of decomposers. CO2 is absorbed by producers, including plants and microorganisms, through photosynthesis. In other words, producers make the vital elements from sunlight and carbon dioxide so that other organisms have food. Consumers, such as animals, eat plants and microorganisms and take the sugars, amino acids, and other essential matters from the plants. As the consumers and producers die, decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, release the carbon from them. The carbon cycle is a crucial process, as it helps to prevent the sun heat from escaping to space and cooling down the earth.
Climate System
Climate is usually referred to as the environmental state of the surface during a prolonged time period (Baede et al., 2018). The climate system is a collective name for all subsystems that affect the climate. Elements of the climate system include atmosphere (all the gases), hydrosphere (the water), cryosphere (glaciers), biosphere (living beings), and land surface. All the elements interact through a wide variety of processes depicted in Figure 2.
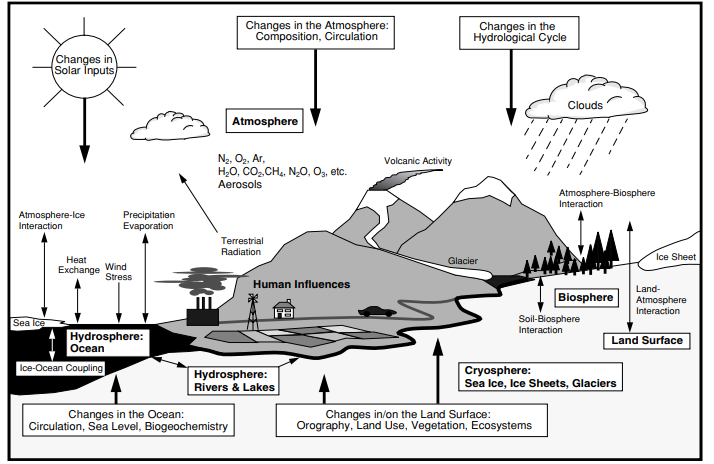
Climate System: Human Impact on Carbon Cycle
Human activities have a significant impact on the carbon cycle. First, we increase the amount of CO2 released into the atmosphere (Baede et al., 2018). Second, we decrease the amount of absorbed CO2 through land-use change (Baede et al., 2018). The increased amounts of CO2 is absorbed by the oceans or remains in the atmosphere (Baede et al., 2018). Increased absorption of CO2 by the oceans leads to their acidification (Baede et al., 2018).
Climate System: Changes in Carbon Dioxide Levels
Human impact on the carbon cycle has tremendously increased the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. According to CO2 Levels (2020), the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere has increased by 60% since 1000 AD. The data demonstrates that the problem of increased carbon dioxide levels is a considerable bother for humanity and can impact the everyday life of people through the greenhouse effect.
Climate System: Greenhouse Effect
The primary danger of increased CO2 is the greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect is the ability of the atmosphere to retain some solar heat (Climate Central, 2014). The heat is retained due to the presence of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. The greenhouse gases include water vapor, CO2, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone (Climate Central, 2014). Increased levels of greenhouse gases warm the Earth and change the climate (Climate Central, 2014). Hence, since human activity contributes to the carbon dioxide levels, it changes the climate on the Earth, which may lead to disastrous consequences.
Land Use Change
Land use change includes all changes in the management of land for different purposes. The most evident factors are deforestation and urbanization (Baede et al., 2018). Deforestation is associated with an increased need in agricultural land to feed the Earth’s growing population. Land use change contributes to the greenhouse effect, contamination, and biodiversity decrease.
Deforestation
Deforestation is the permanent removal of trees to make room for other purposes. Deforestation has increased tremendously during the past 100 years. Experts estimate that currently, the Earth loses a chunk of forests equivalent to a soccer field every second (Mongabay, n.d.). The central factors contributing to deforestation is the production of beef, soy, palm oil, and wood products (Mongabay, n.d.). The current deforestation level alarms scientists, as it damages the environment by negatively affecting biodiversity and the ability to absorb carbon dioxide.
Climate Change: Human Responsibility
Climate change is a result of global warming caused by the greenhouse effect. Some scientists believe that current changes in the climate are natural. However, US fourth national climate assessment confirmed that human activity is responsible for 93%-123% of climate change (Hausfather, 2017). The effect of human activity on climate change was confirmed statistically, which can be seen in Figure 7.
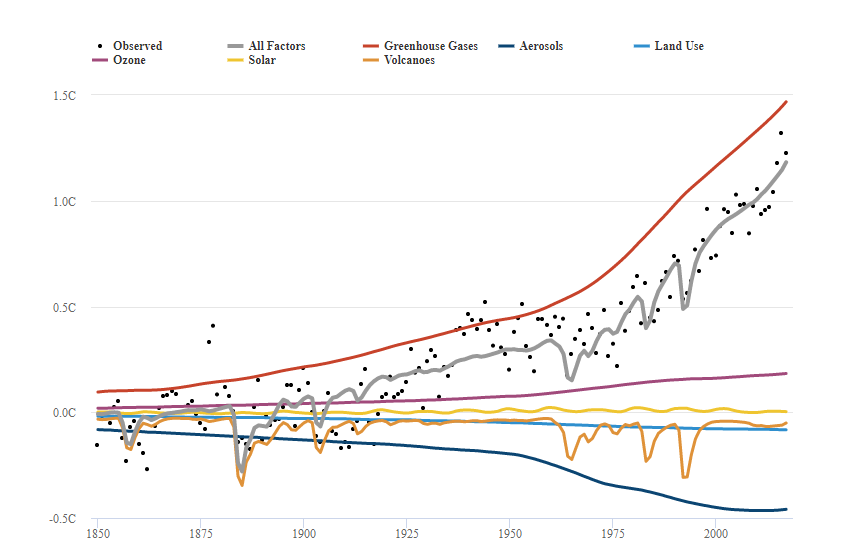
Climate Change: Implications
Climate change is expected to have an enormous effect on all sides of life on our planet. Some of the implications of climate change can be observed now, while others will be observed in the future. Climate change is expected to bring frost-free seasons in unusual areas and increase the overall growing season (NASA, n.d.). At the same time, climate change will increase the number of extreme weather events, including droughts, heatwaves, and hurricanes (NASA, n.d.). The sea level is expected to rise by 1-8 feet, and the arctic will probably become frost-free (NASA, n.d.). The access to freshwater will decrease, and the quality of air and water will go down (NASA, n.d.). This will cause significant problems with public health.
Challenges to Addressing Climate Change
Even though the majority of stakeholders understand the implications of climate change, there are significant problems people encounter when trying to address the problem. There are at least five issues that make it challenging to address climate change. First, CO2 is a global pollutant, which implies that it will do the same amount of damage to the entire planet regardless of where it was released., which makes it difficult to manage and regulate (Baskin, 2019). Second, the effects of climate change remain hypothetical, as the effects will be felt in 50-100 years from now (Baskin, 2019). This creates little incentives for policymakers to address the problem immediately (Baskin, 2019). Third, no direct link can be established between single adverse events and global climate change, which makes it even more difficult to inspire stakeholders to act now (Baskin, 2019). Fourth, developing countries contribute a large share to climate change (Baskin, 2019). The majority of these countries prioritize economic development over fighting climate change (Baskin, 2019). Finally, the modern way of living and values are part of the problem (Baskin, 2019). People will have to sacrifice their current habits to change the situation.
Mitigating the Climate Change: Green Power
Humanity can prevent climate change by turning to renewable energy sources. The common green power sources include solar energy, wind, biomass, geothermal, biogas, and hydropower. The use of green power reduces pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
Mitigating the Climate Change: Dietary Habits
The humanity needs to decrease its meat consumption. Livestock is considered to be accountable for almost 18% of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, as it requires substantial energy to produce feed and fertilizers, breeding activities, electricity use, and resources to build farms (Lacour et al., 2018). Livestock farming is also closely connected to the loss of biodiversity, as natural ecosystems are destroyed be farms used for grass and feed crops (Lacour et al., 2018).
Therefore, a reduction of animal product intake worldwide can sufficiently improve the environmental issue. Food habits of consuming no animal products produce 2.5 times less GHG than diets rich in animal products. At the same time, vegetarian and pesco-vegitarian people contribute 46%-54% less GHG than omnivorous men and women (Lacour et al., 2018). Plant-based products require less land to feed the global population. According to Lacour et al. (2018), a 35% reduction in meat consumption can lead to a 24% decrease in diet-related land use. Thus, dietary habits have a significant impact on the ecological state of the Earth.
Mitigating the Climate Change: Mindful Consumption
Purchasing habits also have a tremendous impact on the environment. Mindless consumption of cheap unneeded products leads to increased emission of greenhouse gasses associated with production that could otherwise be avoided. Additionally, transportation of the unneeded product also contributes to the overall greenhouse effect by burning fossil fuel to deliver these products to the stores. The unneeded goods often end up in the trash shortly after purchase, which inevitably leads to problems with garbage utilization. Currently, global society produces 3.5 million tons of waste daily, and the numbers are expected to grow up to 6 million tons a day in 2025 (Winmark, 2019). A considerable part of this waste is associated with mindless small buys people do to please themselves.
Another purchasing problem is closely related to the current trend of online shopping that was facilitated by COVID-19 pandemic. Consumers all over the world often choose overnight or express delivery for their purchases to arrive as soon as possible. This implies that instead of being delivered in bulks, individual purchases are being delivered with the same heavy-duty, diesel-guzzling vehicles, which are typically used to deliver large orders (Winmark, 2019). Such habits significantly add to the problem of GHG emissions. The same should be said about packaging. Every individual order is heavily packaged to avoid damages to the product. This package is thrown away immediately after receiving the order, which adds to the solid waste production.
Conclusion
Climate is a sensitive system that is being heavily disrupted by human activity. Greenhouse gas emissions and inadequate land use lead to climate change. Climate change is associated with a wide variety of negative implications ranging from an increased number of extreme weather events to the melting of ice sheets. Even though there are significant challenges in addressing the problem of climate change, the global community needs to prioritize is to ensure sustainable development.
References
Baede, A.P.M., Ahlonsou, E., Ding, U., & Schimel, D. (2018). The climate system: an overview. IPCC. Web.
Baskin, K. (2019). The 5 greatest challenges to fighting climate change. MIT Sloan. Web.
Biology Dictionary. (2019). Carbon cycle. Web.
Climate Central. (2014). The greenhouse effect. Web.
CO2 Levels. (2020). Atmospheric CO2 levels graph. Web.
DLA Ignite. (2018). Attention sign. Web.
Go Vegetarian. (2016). Go vegetarian public page. Facebook. Web.
Hausfather, Z. (2017). Analysis: Why scientists think 100% of global warming is due to humans?. Carbon Brief. Web.
Lacour, C., Seconda, L., Allès, B., Hercberg, S., Langevin, B., Pointereau, P.,… & Kesse-Guyot, E. (2018). Environmental impacts of plant-based diets: How does organic food consumption contribute to environmental sustainability? Frontiers in Nutrition, 5, 8.
Lindsey, R., & Dahlman, L. (2020). Climate change: Global temperature. Climate. Web.
Mongabay. (n.d.). Deforestation estimates. Web.
NASA. (n.d.). The effects of climate change. Web.
US Environmental Protection Agency. (n.d.). What is green power? EPA. Web.
Winmark. (2019). How do your shopping habits impact the environment?. Web.
