One of the most salient qualities that a manager must possess is the ability to manage projects effectively. This is increasingly becoming tougher each day in terms of time management and resources involved. The main aspects involved are planning, scheduling, and controlling. A large organization may come up with a given team to foresee the running of projects especially when the work involved is a lot, and successful completion is essential to the firm.
The planning stage starts before the project kicks off; it evaluates the project in terms of cost, time, and labor input. Scheduling the project ensures the implementation of every part of the project within the set period and in the correct order. Organizations popularly use Gantt charts to achieve this. Gantt charts show potential problematic areas thus assisting the managers to tackle them appropriately; however, their sole disadvantage is that they do not give a really clear connection between activities and capital. For cost-effective project management, a voluminous project is subdivided into small portions and even less significant parts assigned to individuals in a team. This is synonymous with the function of Microsoft‘s Windows 7 operating system. Large projects are mainly computerized and use PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Techniques) and CPM (Critical Part Method) software to schedule projects. The latter methods give a better relationship between activities and resources. They give precedence relations and give an idea of how various actions depend on each other.
The controlling aspect sees to it that the project utilizes inputs to a maximum and that the results are of high standards. It also involves relocating funds to other more deserving project areas. Computerized PERM/CPM reports help to realize this. They help in the determination of features such as crucial paths, variance, standard deviation, estimated duration of projects et cetera. A project administrator can determine the probability of completing projects within a given time, and even how to sum up a project within the shortest time possible termed as crashing a project. He achieves all these through manipulation of variables within the project, by either manual calculations, or automated software such as Microsoft Project.
The project manager, who reports directly to the top administration, is in charge of all these operations. He faces significant ethical issues that could compromise his integrity if not careful; therefore, the Project Management Institute’s code of ethics governs his conduct.
Case Study
Network drawing for Hill Company
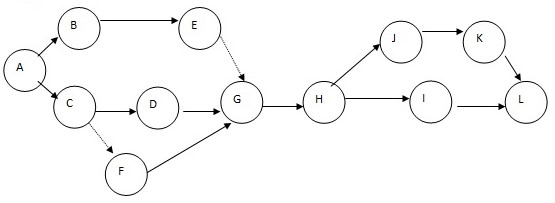
There are two critical paths: A-B-E-G-H-I-L and A-C-D-G-H-J-K-L since the critical activities are A and L. Steps C-F, and E-G are dummy activities hence indicated with dotted lines. Expected activity time t= (a+4m+b)/6, which is [223.2+4(375.2) +552.2] /6.
- T=2276.2/6
- T=379.367 days. The project’s expected length is 379.367 days.
From the expected time t, the probability of finishing the project in 379.367 days is 99% (a=1/100). We calculate the probability of finishing the work in 270 days as:
- P= (270 days*99%)/379.367days.
- P=70.46%
If it were necessary to crash the project to 250 or 240 days, Hill would shorten steps A-B and A-C Since activity A has the least crush cost per day and is a critical step. Using optimistic estimates as crash times, the overall cost would be 5,684,800 dollars, as shown by the following formula:
- Crash cost per period= (Crash cost- Normal cost)/ (Normal time – Crash time).
