Introduction
The role assumed by project managers in the construction field is among the essential factors in attaining a project’s success. However, in recent studies, several complex and large projects face delays. They are overrun in most cases, with the main factors being teamwork, communication, team building, interpersonal skills, and problem-solving. The following paper will be reviewing the framework skills of project managers to improve the complexity of construction projects. An extensive literature review on the project managers’ skills when handling a project will be recognized.
Nevertheless, skills such as actual communication with both the contractors and staff, teamwork, substantial training and planning, and proper resource management contribute to developing a project manager’s skills framework. The following research work findings defended the existing literature on developing the skills of project managers applied by the business consultants and policymakers in untying some of the challenges facing the project in a construction site. The following paper shall also provide some of the challenges facing construction projects besides delivering successful outcomes.
Background
Project management entails monitoring, planning, and controlling the significant aspects of a project, emphasizing all-inclusive project goals in a safer manner, performance criteria, and budgeting. From the following definition, project management emphasizes a project’s performance about the short-term dimensions of a project’s success, cost and quality, and time criterion. Nevertheless, implementing project management practices help attain consistency in a project’s success. A project management’s success is measured during the project’s life cycle through a classic performance measure. Achieving success in building the implementation process is an essential factor in project management. The rate at which projects fail in construction or buildings are abandoned is seemingly retrogressive in developing countries.
Project management can nonetheless be vindicated when evading the essential ills present during the production stages and in the construction industry. For this reason, many projects are prone to either fail or be abandoned. The project managers’ roles arise from the necessity for a technician to take control of the stages in a project’s implementation process. Besides, the project manager should have sufficient knowledge in implementation processes and decision-making processes. For any operation in implementing a project, its success relies on the project manager’s concept of control and appointment of the staff members, time consciousness, and environmental constraints.
Project management has a long history; as witnessed in the construction sector, numerous studies have emerged on planning and success. Gunduz and Almuajebh (2020) concluded that the uppermost one-third of the developments from an arrangement comprehensiveness standpoint at an 82% chance of attaining the set goals. In contrast, at the same time, 66% of the projects available in the lower third met the objectives. Similarly, the results were seen for the design and schedule goals. Zuo et al. (2018) also found out in a construction program study that more effective planning should have a higher criticality index of the deliberated critical accomplishment aspects at 0.870. The intricacy of construction schemes is steadily cumulative, given the new operational and technological initiatives. The project members can identify construction projects identified to be technically complex. Additionally, such a type can be specified upon the absence of a qualified manager to manage new technological involvement recognized by the company.
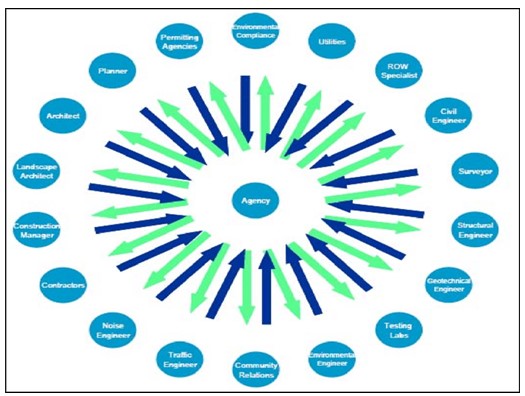
The project’s complexity can also be produced via two significant features: structural complexity and uncertainty. Uncertainty might also be created through the delays in the utilization of construction methodologies or the shape of the required goals (Fadun & Saka, 2018). The complex projects from a different viewpoint can be recognized as developments that demand managers with special managerial and teaching skills, making them capable of showing a high-quality presentation. The project manager’s responsibility is to fire, plan, supervise, and keep both the boss and client in the loop. In this respect, the project managers provide the necessary directions in ensuring that every contributor in every phase of the project identifies their roles. The project managers are majorly committed to the upper management and the outside clients and vendors as expected (Tsiga et al., 2016). The figure above illustrates some of the construction project’s activities without having the project manager or the construction agency undertaking a task (see. fig. 1)
It has been argued by Tsiga et al. (2016) that every organization is more prone to face the challenges imposed by continuous changes in coping with new technology innovations that aim at enhancing organizational performance. This is most likely to expect an extremely committed manager and hard-working with strong planning abilities that are most likely to enable the manager to adapt to nature and project complexities. Several research types point out numerous factors that contribute to the success of more complex projects. Although, among the most common and essential elements in the project manages role. The multifaceted projects will need high skilled management and persons that are knowledgeable in heading the project. There needs to be a super-strong connection between a project manager’s skills and other rudiments of the project, which will ensure the emergence of successful outcomes.
A project will be termed as successful once it passes the four success test criteria such as the time criteria, cost criterion, and effectiveness criterion; however, the significant measure is completed according to the original set performance and the quality standards. The success criterion calls for more successful project implementation by utilizing the already proven techniques in management, planning, directing, controlling, and organizing. The project manager should consider project choice resulting in good project selection alongside improving a successful project’s probability.
Source of the Idea
All stakeholders do have a role to play towards the growth of a construction farm. Contractors, clients, and the government have an obligation of leasing the essential changes with the project managers mandated to represent contractors of clients at the various levels of a project are in a unique position to enable the change the industry from the grass-root level. In the construction industry, the project managers are answerable for the general accomplishment of bringing the owners physical growth within the constrictions of time, cost, safety, and environmental expectations (Tsiga et al., 2016). Project managers should be technically competent to adapt to the rapidly changing industry by depending on skills and knowledge attained through experiences and training. Besides, project managers also need to supplement with non-engineering skills and expertise to achieve the changing responsibilities.
The project managers’ role is to distribute and create knowledge to identify obstacles to knowledge acquisition. Besides this knowledge role, it is noticeable that knowledge management in improving project management’s performance and competence is rarely brought to discussion. Besides, there is no identification in the actual project management practices to enhance knowledge management (Fadun & Saka, 2018). However, the administration of knowledge in project-based businesses such as that witnessed in the construction industries faces challenges rarely faced by the non-project industries.
In most cases, individuals for various companies join hands as a project team, which is essentially a temporary organization. This implies the need to create the right knowledge-sharing culture that will provide room for contact to detailed expertise from various sources and access alongside assuming learning from different projects. Nevertheless, most learning prospects remain tactful and retained in individuals’ memories (Tsiga, Emes, & Smith, 2016). Additionally, the predominant supply chain, including the construction farm’s procurement practices, discourages effective learning practices. Instead, the construction industry gives room to continue coming up with progressive ideas and proper methods that are wasted by not repeating upcoming projects. The project managers’ primary errands include controlling the physical and financial resources in a construction site to bring the project to a fruitful conclusion regarding time, the satisfaction of the relevant stakeholders, and cost.
Nature of the Opportunity
Several research findings propose that the project managers should have highly successful that should be possessed to achieve and manage the projects more successfully. The manager should also use the manual on the “Project Management Body of Knowledge: as a guide; this will assist and guide them in their complicated management journey. The manual is specialized for applications within the country; this positively takes esteem and is essential to project managers on a global platform. The following also examines why numerous individuals and institutions concerned in managing projects and contacting sectors remain concerned in the Project Manager Plan certificate (Fadun & Saka, 2018). Having the project executives with a Project Manager Plan follows the management procedures as characterized by professional-managerial skills. This is to maximize the success chances of a project, alongside ensuring that the managers’ appropriateness and success in handling more complex projects where large investments are annually pimped in planning and implementation.
Managers’ use guide should also define an operative PM (Project Manager) features, including performance, individual, and knowledge. Besides, knowledge will infer to the PMs owned information about the management of a specific project. For instance, will the project manager advance a plan in addition to being able to draft a project’s schedule? Similarly, personal infers to a project manager’s personality, his/her attitude, and leadership (Tsiga, Emes, & Smith, 2016). This can also be obtainable in connection with the manager’s significant relation to the stakeholders with whom should be interacted. However, other guides also describe over eight managerial and interpersonal administrative skills that should be influenced by administrators of the project to manage the tasks more effectively and successfully. Such skills are motivation, leadership, influencing, communication, cultural and political awareness, negotiation, and decision making.
Interestingly, a significant number of the mentioned traits are related to a manager’s capacity to motivate others to pursue that which is deemed
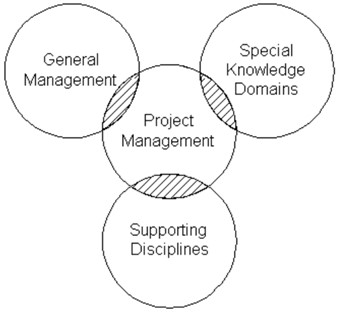
Necessary for the administration and budgeting of the project. Similarly, the ability to influence others is imperative because the project managers lack formal authority over the employees they work with (Fadun & Saka, 2018). Other skills that will guide the project manager to manage complex construction projects include leadership, Persistence and Decision making, self-awareness, flexibility, quick thinking, honesty and integrity, creativity and imagination, and intelligence (see fig. 2).
Expected Challenges
The traditional practices by project management have evolved as the requirements for control and manage construction projects unfold. Nevertheless, with management techniques and ICT advances, the conventional approaches have proven insufficient in locating new task necessities. Projects in construction are designed by various designers positioned in different geographical locations, managed, and procured by the new partnering strategies. Materials used in a construction site should be purchased and delivered via a strategic alliance with the suppliers. Such construction industry changes have also highlighted numerous weaknesses in project management’s traditional practices (Fadun & Saka, 2018). The clients, government, and industry aim to bring about the construction sector changes and improve profitability, quality, and competitiveness and increase the client’s values in cases where the emphasis is on managing the interface between the client’s organization and the project. Such old traditions have contemporarily shifted towards managing the flow of activities through a project’s life cycle.
The project managers engaged in the complex projects are expected to have full services to handle the various teams and partakers. It is possible to see that they possess the highest position and remain essential to a project’s success. Nevertheless, similar to any other field, project managers face many challenges that, in most cases, result in the failure or collapse of a project. A construction project manager will face many challenges during each face of the project life cycle. Nevertheless, they need to maintain high standards of professional and personal conduct. The challenges faced include but are not limited to
- Poor Team Skills,
- Inadequate Communication,
- Lack of accountability,
- Scope Creep/Scope changes,
- Lack of stakeholder engagement, and Impossible deadlines.
Inadequate Communication
In most cases, the current practices in project management are isolated and are concerned with managing challenges related to individual stages of a project. Additional expenditure brought about by reworking is likely to yield the following challenge. The reworking problems occur due to contradicting information and the failure to receive a piece of the given information in time. The primary cause is inconsistency in data flow between the various parties pertinent to the construction project. Close to 30% of the construction reworks are attributable to the processes connected to the challenges (Zuo et al., 2018). For instance, a client might frequently come up with changes to designs without communicating effectively to both the subcontractors and contractors for such changes to be implemented effectively, in most cases resulting in reworks. In most cases, this results in many financial constraints from the client.
Furthermore, the lack of integration with the supply chain results in challenges with communication. The ordering, invoice practices, and purchasing have many inadequacies relating to delays in supply reception, less collaboration with the suppliers and manufacturers, and low integration of purchasing accounts. For example, the various delays are most likely to implement the current procurement material systems that do not integrate with project schedules and plans. Lack of an integrated procurement system affects construction firms’ stock control policies due to the absence of accurate resource prediction. The primary reason for this will be poor coordination and communication among the supply chain partners and an integrated system to stand out for such needs.
Introduction of Automation in Management Practices
Although most construction firms have adopted IT in improving specific applications/ applications, the construction industry remains to traditionally hold the perception of using hard copy documents compared to using electronic forms for record purposes and auditing. Most of the construction industry’s communication problem is structural challenges (Tsiga, Emes, & Smith, 2016). In this respect, the company’s management should also ensure that the drawings are amended and confirmed with the drawings receipts confirmed by the contractors in writing. A higher percentage of the available project management software emphasizes tasks such as monitoring and project planning, risk management, cost control, and scheduling, among many more. Such isolated applications tend to result from a widespread of stand-alone application packages with fixed communication links.
Lack of a Standard Process in Management
Even though initiatives are implemented in standardizing project management processes such as the project management interventions, projects are managed to depend on the experience portrayed by the project managers appointed for the specific tasks. However, project managers within the same organization would prefer to follow their expertise developed over a more extended period (Tsiga, Emes, & Smith, 2016). Such practices within an organization are likely to result in variations in management practices, thus creating an essential impact on controlling and coordinating project information. It is without a doubt that the majority of SMEs fail to afford research and development. In new technologies, however, access to project webs can be attained for them to be competitive. However, SMEs are indirectly obliged to do so whenever they participate in complex project management. Other participants are expected to use collaboration tools for company management and manage the project.
Resources Available
In team productivities, the resource teams for every activity in a construction site are formed to override the efficiency of resources while at the same time repeatedly performing similar tasks. A team’s productivity can be attained from research observations, methodology databases, experiments, and case studies. Team productivity is always dependent on the combination of human resources and machinery; hence, the productivity of both the human resources and machinery is still respectively determined (Tsiga, Emes, & Smith, 2016). An optimum team capacity is obtained by merging a much more reasonable and logical machine and human resources. This is identified as the optimum machine/labor ratio. Generally, the machinery productivity is always estimated through using the formula stated as
![]()
Conversely, Human Resources Productivity would also be determined by applying the formula:
![]()
The productivity of resources identified is the productivity selected to execute a task. Resource productivity in planning management tends to be much greater than the minimum productivity expected in completing a task. Nevertheless, the minimum productivity will also be the lowest in completing a given task in time. Depending on the project team, the planner or project manager can identify each activity’s duration (Tsiga, Emes, & Smith, 2016). The period is then subjected to the methodologies in a project and the essential techniques for estimating a given duration of a project; this will vary depending on the situation, type of work, schedular, and other factors. Nonetheless, the project manager should also consider the conditions of a contract, its complexities, risks, resource constraints, and latent requirements, among many others. Minimum productivity calculated as:
![]()
The amount of time needed in completing an activity in every stage of the project is then added and identified as the overall duration in completing a given task. The activities are then merged in a logical relationship that is then analyzed from the consequence analysis. The concept of line balance can then be implemented by placing a lead and lug duration between different activities, overlapping together. This occurs without tampering with the progress and being that they are most likely performed in various locations. In determining the total duration needed in completing a project and realizing that the whole time exceeds the period specified in the contract, then the critical activities’ productivity is increased. For the project manager to be a successful and respectable leader, he/ she needs to have the following attributes (Zuo et al., 2018):
- The project manager should understand the weaknesses and strengths of their team and be good listeners.
- A successful project manager should be able to manage people alongside being able to form a team.
- The project manager should also be conversant with the corporate groups that play a decisive role in its success.
- The project manager should understand the structure in which the company operates and every department’s functions within the construction farm.
- With kind or harsh words, the project manager should also know how to motivate its team.
- A project manager should always be careful with criticism of any kind (fashion or culture etc.)
- One should understand the project being managed in detail.
- One does not have to be a genius since there will be superintendents and engineers working on the project.
- The project manager should learn to communicate with the contractors and exercise fairness and be at the forefront of protecting its interests and goals.
- By leading as an example, the project manager should have open-door policies.
- The project manager must earn respect and have some level of charisma to enrich one’s reputation.
- The project manager should learn when to listen and when to speak.
- The project manager should follow the companies’ standards since they are set in place to make work easier. In most cases, the project manager should not act against a company’s set rules; instead, consider getting approval to deviate from the established guidelines due to the geographical location or the site environment. In such a case, the approval sequence should also be followed within the corporate groups. In this case, no reason should crop up.
The labors’ level of skills also contributes significantly to a project (Zuo et al., 2018). Development and training can both be defined as creating work-related skills and knowledge for the subordinates. Additionally, the extension of personnel’s movement also contributes to the human resource growth extension of an organization. Training has even to start by highlighting training needs through performance assessment and analysis of an organization.
Conclusion
In the construction industry, project managers play an important role in its growth. In most cases, the successful project managers end up as senior managers in their organizations, responsible for the strategic and policy decisions. Project managers bring a positive mindset and attitude to various projects and improve the whole industry in the long run. Traditionally, project managers have to control time, cost, safety, quality, and environmental issues. By supplementing their roles as drives of change and ensuring continuous development of the construction industry, the project managers should ensure that they are up to date with the new technological developments in the construction sector. The expansion of existing roles can only be identified in the construction managers’ awareness of the construction industry’s requirements. Hence, the industry’s long-term policy and vision should be critically announced publicly to enable other stakeholders to reflect on it and come to conclusions.
References
Fadun, O. S., & Saka, S. T. (2018). Risk management in the construction industry: Analysis of critical success factors (CSFS) of construction projects in Nigeria. International Journal of Development and Management Review, 13(1).
Gunduz, M., & Almuajebh, M. (2020). Critical Success Factors for Sustainable Construction Project Management. Sustainability, 12(5), 1990.
Shibani, A., & Sukumar, D. (2015). The role of the project manager in construction projects in India. The China Business Review, 14(6), 298–324. Web.
Tsiga, Z. D., Emes, M., & Smith, A. (2016). Critical success factors for the construction industry. PM World Journal, 5(8), 1–12.
Zuo, J., Zhao, X., Nguyen, Q. B. M., Ma, T., & Gao, S. (2018). Soft skills of construction project management professionals and project success factors. Engineering, Construction, and Architectural Management. Web.
