Introduction
Project background
The Australian government is cognisant of the role of infrastructure in supporting product and service delivery and improving the country’s productivity. After the industrialization epoch, infrastructure development became part of any meaningful economic growth due to the necessity to transport goods and workforce. Consequently, the Australian government is committed to investing in the development of new infrastructure in all states. In line with the country’s infrastructure agenda, the Australian government intends to construct the East-West Link, which is an 18 kilometers road linking the Western Ring Road and the Eastern Freeway. The road will pass through Melbourne and it is expected to address the travel needs between the eastern side and its western counterpart. The Victorian State Government has committed itself to constructing Stage 1 of the project, which will entail building a road that will link the Eastern Freeway and the CityLink. The cost of the first stage of the project is estimated to be $6-$8 billion. The Victorian government has allocated the cost of the first stage in its 2013/2014 budget. The work is expected to start in late 2014 and end by 2019/2020 (Loughnane 2013). In May 2012, the Victorian government publicized its objective to kick-start the planning phase of the East-West Link project.
Aim
This report outlines the planning phase of the East-West Link project to facilitate its commencement. The report outlines the project fundamentals, project techniques and tools, project complexity, project law, project finance, and project methods.
Project Fundamentals
A number of project-management knowledge areas will be taken into account in the process of planning the project. Some of these areas are discussed herein.
Project vision
To improve the country’s road network to achieve an excellent transport network.
Project objectives
- To reduce congestion between the Eastern Freeway and the Western Ring road
- To achieve more efficient freight and travel systems
- To improve the country’s competitiveness by supporting economic growth in Victoria
Project assumptions
The following assumptions will be made in the course of implementing the project.
- The project will be fully sponsored by the Australian government, which will entail ensuring that the funds necessary to implement the project are availed
- The estimated cost of the project will not change due to changes in oil prices and other external factors.
- The project will gain the approval and support of all the stakeholders such as environmental activists and the relevant government ministries.
Project constraints
Project implementation faces various constraints that limit the process (Adams, Means & Spivey 2007); however, with the correct mitigation measures put in place, the implementation phase becomes one of the easiest phases as it entails the execution of the already laid out plan. It is imperative for the project manager to understand the specific constraints that will be encountered in order to integrate effective management strategies. The East West Link project will face two main constraints, which relate to time and cost. The project is expected to commence in 2014 and end by 2019/2020 as aforementioned. Failure to complete the project within the set timeframe will lead to an increment in the cost of the project. The estimated cost of the project may increase due to other external factors such as various economic factors such as inflation and the occurrence of economic recession. However, adjusting the cost of the project upward will be challenging. According to Loughnane (2013), governments are required to utilize the taxpayers’ money effectively. The Australian government has estimated that the first stage of the project will cost $6-$8 billion. Consequently, the project manager will be required to ensure that this amount is not exceeded.
In addition to the above constraints, the road construction project will also be required to adhere to acceptable levels of noise. To achieve this goal, the contractor will be required to integrate a noise management plan. The plan will outline the steps that will be taken in order to minimise noise.
Project scope
The project manager will ensure that adequate scope management is undertaken. This goal will be achieved by taking into account a number of elements, which include project initiation, defining the scope, scope planning, verification, and change control. Before implementing any project, it is paramount for the project manager to ensure that the necessary authorisation is obtained (Wysocki 2004). A comprehensive project team comprising of the Project Manager and a Project Board will be constituted.
Project Managers should ensure that the project scope is well defined. Defining the project scope is essential in improving the project outcome (Wiegers 2008). Consequently, the target audience level of satisfaction is improved. According to Ghuman (2010), scope definition entails integrating a comprehensive work breakdown structure. Thus, one of the issues that the project manager should consider is dividing the entire East West Link project into small components. Stage 1 of the project will entail constructing a 6 kilometres road. The stretch will begin at Hoodle Street and end at the CityLink. The following work is expected to be undertaken in the first phase.
- Construction of a crossing point at the Elliott Avenue as this interchange will play a critical role in improving the connection between the East Freeway and the West Ring road through the tunnel.
- Construction of a new bridge to facilitate movement of traffic between Hoddle Street and the Eastern Freeway
- Construction of an entrance into the underground tunnel just past the existing Eastern Freeway
A number of activities will be undertaken in the process of defining the scope. They include:
- Project documentation
- Developing a project management plan
- Sequencing the road construction activities
- Estimating the duration
- Designing a schedule
- Planning the risk management strategy
The flowing chart illustrates the scope data flow diagram to be used in the process of defining the project’s scope.
The project manager will ensure that a comprehensive verification of the project scope is undertaken. Scope verification aids in ensuring that the target client and the sponsor accept the project. The verification process will be aimed at ensuring that there is no goal or role overlap in the process of implementing the project. Moreover, scope verification will also aid in strengthening and reinforcing the project scope (Cobb 2012). The occurrence of change cannot be ruled out in the process of implementing the project. An effective scope change control will be undertaken and it will entail evaluating the impact of change on the project’s work breakdown structure. Scope change control will create a perfect opportunity for the project manager to receive requests on possible changes on the WBS. According to Adams, Means, and Spivey (2007), the objective of initiating projects is to achieve specific predetermined objective. However, occurrence of change may hinder the achievement of the desired outcome, which underscores the importance of integrating effective scope control mechanism. The project manager will ensure that possible variances that might occur in the project implementation process are identified for such a move will play a critical role in incorporating the necessary adjustments.
Project deliverables
Every project must have specific project deliverables. The deliverables refer to specific outputs that must be attained in order to complete a particular task successfully. According to Satzinger and Burd (2008), project deliverables vary depending on the type of project. Examples of project deliverables include project design documents, and project prototypes. In the process of implementing the East-West Link project, the Australian Government intends to achieve the following deliverables.
- Developing a need analysis document – This document will outline what the Australian government intends to achieve by constructing the East West Link. Some of the issues cited in the need analysis document include the need to improve travel time, reducing congestion and to enhance travel and freight networks.
- Commencing the contracting process– Upon completion of the road design phase, the government will issue tenders to the most competent road contractor. This will be achieved through the process of bidding. The contractor will be selected by assessing their past performance. Moreover, the Australian government will also evaluate the total projected cost of the road construction process. The contractor selected will have a significant impact on the quality of the road constructed.
Project acceptance criteria
Before commencing the project, a comprehensive evaluation on the impact of the project will be conducted by assessing the long-term and short-term impact of the project. The cost benefit analysis will aid in determining the suitability of the project to Australia’s economic growth. By endorsing the East West Link project, the Victorian Government estimates that the road construction project will benefit the government by $1.4 for every $1 invested in the project. Consequently, the Australian government expects that the road construction will improve the country’s productivity. Upon its completion, the government will undertake an analysis of the project in order to determine whether its utilisation have translated into the estimated benefits.
Moreover, acceptability of the project will also be determined by assessing the environmental impact of the road. Road constructions that have adverse effect on the environment such as by destroying the delicate ecosystem should be re-evaluated prior to their commencement. The project’s acceptance criteria will also be based on the effectiveness of the road in linking the East and the West road systems and its ability to reduce congestion.
Project approval
The project documents will be sent to the appropriate government ministries for approval. The Road Ministry is one of the ministries that will be required to approve the project.
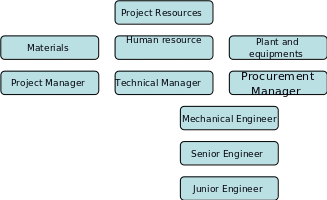
Project resources
The success of the project will be influenced by the availability and quality of various project resources. Some of the resources that will be taken into account include human capital, finance, plant, equipment, and facilities. It will be ensured that the necessary road construction equipments such as earthmovers are available. Sufficient supply of the necessary road construction materials such as bitumen, cement, ballast and the best type of soil will be ensured. Moreover, it will be ensured that the project has the necessary human capital in order to improve the output. The project’s human capital will be sourced from various departments in the Road Ministry, the Land Ministry and other relevant ministries. Human capital will also be sourced from external sources such as road construction consultants. However, it will be ensured that only professionals are incorporated in the management of the road construction process. Examples of such professionals include architects, accountants, and engineers. Moreover, other skilled and semiskilled labourers will also be incorporated in the project. Prior to its commencement, it will be ensured that the government has supplied the necessary funds. This will aid in ensuring that the project is completed within the set timeframe. The chart below illustrates the project resources.
Project time management
The objective of designing and implementing projects is to achieve particular economic or social objectives. Consequently, it is imperative for projects to be completed within the set timeframe (Kerzner 2009). The scarce characteristic of time underscores the importance of effective time management. Westland (2007) defines time management as “the process within which time spent by staff undertaking project tasks is recorded against the time” (p.10). Time management provides the project manager with an opportunity to control how resources are utilised (Taylor 2008). Consequently, the project manager is in a position to minimise the likelihood of the project experiencing cost increment (Satzinger & Burd 2008).
The Victorian State government expects that Stage one of the project will be completed within the set timeframe. However, a number of activities will be taken into account in order to facilitate this goal. The chart below illustrates the specific activities and the respective timeframe.

The project manager expects that the project will be completed within the set period.
Project schedule
The project manager expects that the project will be completed within the set timeframe. In an effort to ensure that the project is effectively implemented, a comprehensive project schedule will be incorporated by breaking won the project into a number of components. The Gnatt chart below illustrates the East West Link project schedule. The specific milestones to be achieved are clearly outlined.
Contract administration will entail awarding the road construction contract to the most qualified contractor. Moreover, it will also entail administering and managing the entire road construction project. The environmental work will entail measuring and determining the impact of the road construction project on the prevailing ecosystem such as flora and fauna. Traffic management will entail the strategies that will be implemented in order to support free flow of traffic between the existing junctions. Adjusting, relocating, and diverting public utilities such as power lines, draining systems and pavements is expected to consume a substantial amount of time as illustrated by the gnatt chart above. Other road construction activities that are expected to consume a substantial amount of time include installing road lightings, traffic signs and marking the road. The final stage will entail finalising the road construction and handing over the road to the government.
Project financing and cost management
Effective cost management is vital in the process of implementing a particular project (Project Management Institute 2000). This assertion arises from the fact that cost is one of the major constraints that project managers must adhere to in the process. In an effort to ensure that the first stage of the East West Link is effectively implemented, the project manager will incorporate the concept of cost management. This aspect will play a critical role in ensuring that the Victorian and Australian taxpayers obtain value for their money. In an effort to ensure that the project does not stall due to shortage of funds, the Australian government will set up a Funding and Financing Unit. The unit will be charged with the responsibility of advising the Victorian State government on the most efficient alternative to raise capital for the project.
A comprehensive cost management plan will be incorporated. The plan will be comprised of an outline of the project’s resource planning, cost budgeting, cost control, and cost estimation. According to Nevitt and Fabozzi (2000), resource planning is comprised of a number of activities such as estimating the necessary resources and the quantities required. The main elements identified in the resource-planning phase include the tools and equipments, materials, services, and the human capital required to perform the necessary project activities.
Estimating the cost of the project is paramount in the process of obtaining funds from project sponsors (Yescombe 2002). One o the most effective tools that project managers can use in their quest to estimate the cost of the project is the financial plan. The financial plan assists the project manager in identifying the various cost elements that will be incurred in every stage of the project, which gives an idea on the total cost of the project. According to Westland (2007), one of the most important elements in the process of managing project cost is ensuring that the various project activities are maintained within the set budget. This aspect underscores the importance of integrating optimal cost control measures. The Victorian Government will fund the first stage of the project. The government estimates that this phase will be completed at a cost of $6 to$8 billion, which is the amount that the Australian government has allocated the project in its 2013/2014 budget.
In order to minimise the likelihood of the project stalling, the Australian government will undertake a comprehensive project cost estimation, which will be achieved by adopting the reserve contingency analysis. The reserve contingency analysis will aid in integrating the uncertainly that might affect the cost estimates by incorporating a contingency amount into the estimate value. Twenty five percent of the estimated project cost will be added to the project budget as the contingency value. The additional amount will act as a cost buffer to the East West Link project budget. The contingency amount for the project will be adjusted as the project progresses, which will play a critical role in ensuring that the project’s financial resources are effectively utilised. The chart below illustrates the estimated project progress with regard to fund utilisation.
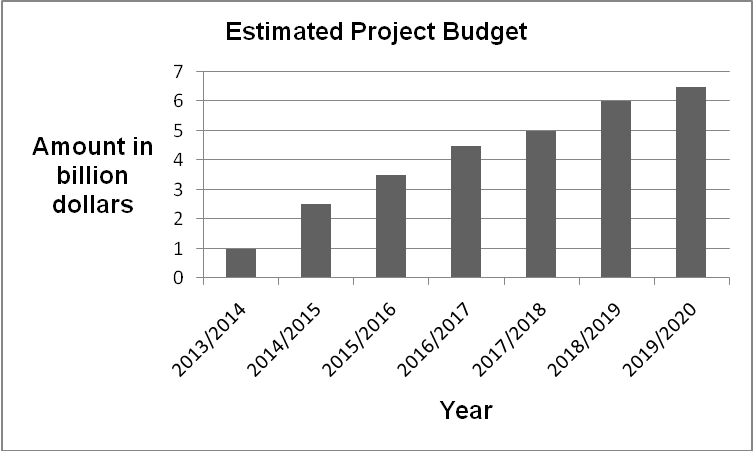
The project manager will ensure that effective cost control is undertaken. This will be achieved by assessing funding requirement, establishing the cost baseline and expenditures. Cost control will play a critical role in determining whether the project is progressing in accordance with the set cost, scope, and time.
Quality management
The Australian government is committed towards ensuring that the East West Link road contributes towards improvement of the country’s transport network. Moreover, the government projects that the users of the road will be satisfied. However, in order to achieve this goal, effective quality management has to be undertaken. Therefore, the project manager will incorporate the concepts of quality assurance, quality control, and quality planning. Quality planning entails identifying the relevant quality standards that should be adhered to in the process of implementing the project. The Project Manager will ensure that the project is implemented in accordance with the set procedures and policies. Moreover, the project manager will ensure that the project complies with the set project requirements.
In a bid to improve the outcome of the project, the Project Manager will follow a comprehensive quality management plan. The plan will be comprised of project deliverables and processes. The manager will evaluate the set deliverables in order to determine whether they comply with the standards defined by the Australian Road Transport Authority. Moreover, quality control will ensure that the East West Link road project contributes towards a high level of satisfaction amongst the target audience. The project manager will be required to ensure that the East West Link road is of high quality. Consequently, high quality materials should be used in the process of implementing the project.
In a bid to ensure that the quality of the project is determined effectively, a number of tools will be integrated. Some of the tools that the project manager should consider including in conducting a cost-benefit analysis of the entire project, control charts, benchmarking, and determining the cost of the quality (Rad & Levin 2003). A survey conducted by the Victoria State government shows that the East West Link has a benefit-cost ratio of 1.4, which shows that the project will lead to attainment of high net economic benefit. Moreover, the government notes that the project has a 9% internal rate of return. The Project Manager will compare the actual outcome against the government’s projection.
Project Risk
According to Rose (2005), all projects involve risk. Consequently, it is paramount for the project manager to integrate the concept of risk management. Failure to manage project risks may lead to the project becoming doomed. Project managers must be proactive in identifying risks, as this move aids in integrating effective measures to counter the risk. In the course of constructing the East West Link road, the project manager is cognisant of the existence of a number of risks that might affect the project outcome. These risks include the risk of budget loss, resource conflict, time conflict, over-budget, and resistance from the community. Resistance from the local community within which the East West Link will pass through is one of the major challenges the project manager will face. According to Schneiders (2013), a group of individuals in Victoria have vowed to protest the construction of the road. The protesters plan to chain themselves to the road construction machinery. Such protests may hinder completion of the road within the set timeframe.
The project manager is also cognisant of the fact that the project may suffer a drawback due to budget loss. Budget loss occurs if the cost of the project is higher than what was earlier estimated. In an effort to limit the occurrence of budget loss, the Victorian State government has estimated the cost of the project to be between $6 and $8 billion, which means that the government has given the project a high strategic value. However, if the cost of the project exceeds $8 billion, the Victorian State government may not be in a position to fund the project to its completion due to shortage of funds. In the event of budget loss, the Victorian government will be forced to consider seeking finance from other private and public partners.
Time conflict originates from poor time allocation and to eliminate time risk, the project manager will ensure that the optimal time allocation to various project tasks is undertaken. This goal will be achieved by integrating the Microsoft Project Server. The software will play a critical role in managing time. For example, the software will aid in identifying critical path to the project. On the other hand, Microsoft Excel will be used in the process of dealing with the risk of over-budget. The project manager will be in a position to estimate the cost of the project effectively.
Project communication
Communication management is fundamental in the implementation of projects. According to Schwalble (2009), project communication management plays an essential role in ensuring timely effective and efficient generation and utilisation of project information. In a bid to improve the outcome of the East West Link road project, the project manager will ensure that effective communication is developed and sustained throughout the project, which will be achieved by integrating the concept of communication planning. The project manager will assess the communication and information needs of all the relevant stakeholders. Some of the stakeholders to who will be considered in the process of designing the communication plan include the project teams, project sponsors, and the various regulatory authorities in Australia. In a bid to achieve efficiency and effectiveness in the process of distributing information, the project manager will utilise various communication mediums. The project manager will be required to incorporate optimal performance reporting by disseminating status and progress reports (Schwalble 2010). Moreover, the manager will undertake administrative closure by disseminating information regarding completion of project phases.
Project procurement
The Victorian Government is committed towards ensuring that the outcome of the East West Link road project is of high quality and to achieve this goal, effective procurement management will be integrated. The project manager will ensure that building materials are procured from certified suppliers through solicitation of quotations and bids. A number of procurement elements will be taken into account in the process of selecting the supplier. These principles include ethics, fairness, transparency, accountability, effectiveness, efficiency, and competitiveness.
Project human resource management
The success of stage one of the East West Link project will be influenced by the quality of the human capital. A comprehensive human resource plan will be designed. The plan will outline the reporting relationship amongst the various project team members. Other activities that will be undertaken in order to improve human capital include assigning project roles and responsibilities. Moreover, the project manager will ensure that only qualified individuals are incorporated in the team. The project manager will focus on developing a strong team by nurturing individual and group skills. As a result, the project manager will be in a position to improve the project teams’ performance and hence the outcome of the project (Dinsmore & Cabanis-Brewin 2011).
Project complexity
Curlee and Gordon (2011) define project complexity as “a measure of the inherent difficulty of delivering a project, which varies widely not only in their overall level of complexity but also in what drives that level” (p.12). The success with which the first stage of the East West Link road will be implemented will depend on the degree to which the project manager and other stakeholders cope with the complexities that arise. The East West Link road is categorised as a national project based on its economic significance to the country’s economic growth. Additionally, the project can be defined as complex considering the fact that it entails connecting other existing road networks and cities in Australia. A large number of individuals in the local community will be affected by the project. Some individuals may perceive the costs of the project to be more compared to the benefits, which may prompt resistance from some stakeholders. Therefore, based on the Helmsman Complexity Scale, the project can be ranked between 7 and 9 points. The complexity of the project is well illustrated by the resistance of the local community in Victoria. Such resistance may hinder the project’s implementation process.
By understanding the complexity associated with the project, the project manager will be in a position to incorporate the necessary control mechanisms. Moreover, understanding project complexity will enable the project manager to hire the most qualified capital. For example, the project manager and the relevant regulatory authorities will be in a position to involve the local community and other interest groups. This move will play a critical role in minimising resistance towards construction of the East West Link.
Project Law
The construction of the East West Link aims at benefiting the public by easing congestion. Moreover, the project will be funded using taxpayers money in Victoria State, which underscores the importance of ensuring that the legal funds allocated for the project are utilised effectively. The project manager will ensure that the concept of legal project management is incorporated, which will aid in ensuring that the project implementation processes are consistent with the set structure. Some of the aspects that will be considered include ensuring optimal project initiation by defining the project, the desired outcome, project scope, and the goals. Additionally, the project should comply with the laid out project plan, which will enhance the effectiveness with which the set deliverables are attained. The project law should also outline the appropriate human capital to be incorporated in the project. Other elements that should be included in designing the project law include the execution, monitoring, and evaluation plans. By following the project law, the likelihood of the project being completed successfully is high.
Conclusion and recommendations
This report outlines the core project principles that will be taken into account in the process of constructing Stage 1 of the East West Link road. A clear definition of the project vision, objectives, assumptions, and constraints is vital in motivating stakeholders to be committed towards the project. Moreover, the success of the project will be determined by the effectiveness and efficiency with which the various project-management knowledge areas are defined. Integrating the knowledge management areas will aid in improving the outcome of the project. Consequently, a high level of satisfaction amongst the target audience will be achieved. In addition to satisfying the target audience, the Australian government will achieve a great milestone towards good and service delivery, which form a critical part of any meaningful economic growth.
The Australian government is of the opinion that the project will contribute towards improvement in the country’s road network, which will stimulate the country’s economic growth. However, in order to achieve these benefits, it is paramount for the following issues to be taken into account. First, the project manager should ensure that the complexities associated with the project are well understood to aid in formulating effective mechanisms to deal with project complexities. For example, the Victorian State government should let the local community understand the benefits associated with the project. This understanding will play an essential role in minimising resistance. Secondly, the project manager should review the progress of the project continuously in order to identify possible gaps.
Reference List
Adams, T, Means, J & Spivey, M 2007, The project meeting facilitators: facilitation skills to make the most of project meetings, John Wiley, Hoboken.
Cobb, T 2012, Leading project teams: the basics of project management and team leadership, Sage, California.
Curlee, W & Gordon, R 2011, Complexity theory and project management, Wiley, Hoboken.
Dinsmore, P & Cabanis-Brewin, C 2011, The AMA handbook of project management, American Management Association, New York.
Ghuman, K 2010, Management: concepts, practice and cases, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi.
Kerzner, H 2009, Project management a systems approach to planning, scheduling and controlling, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Loughnane, B 2013, Building Melbourne’s East West Link. Web.
Nevitt, P & Fabozzi, F 2000, Project financing, EuroMoney, London.
Project Management Institute 2000, A guide to the project management body of knowledge, Electronic Imaging Services Inc., Arizona.
Rad, P & Levin, G 2003, Achieving project management success using virtual teams, J. Ross Publishing, Florida.
Rose, K 2005, Project quality management; why, what and how, J. Ross Publishing, Florida.
Satzinger, J & Burd, S 2008, Systems analysis and design in a changing world, Course Technology, Cambridge.
Schneiders, B 2013, Hit the road, locals tell east-west plan.
Schwalble, K 2009, Information Technology: project management, Cengage Learning, Ohio.
Schwalble, K 2010, Information technology project management, Cengage Learning, Boston.
Taylor, J 2008, Project scheduling and cost control: planning, monitoring and controlling the baseline, J. Ross Publishing, Florida.
Wiegers, K 2008, Practical project initiation: a handbook with tools, O’Reilly, New York.
Westland, J 2007, The project management lifecycle: a complete step-by-step methodology for initiating, planning, executing and closing a project successfully, Kogan Page, London.
Wysocki, R 2004, Project management process improvement, Artech House, Boston.
Yescombe, E 2002, Principles of project finance, Academic Press, Boston.
