Step 1
The key problem with solar power that has discouraged its use is the fact that its technology is still very expensive and unreliable. Compared with the use of hydro, nuclear, geothermal, and coal, the use of solar power has not been widely embraced (Armentrout 24). The popularity of solar energy is still lower because its technology is still uncompetitive and is subject to weather variations.
The history of solar energy can be traced back to the earliest civilizations. However, it should be noted that solar energy has been utilized as a source of electricity since the 19th century. In the year 1840, Alexander Becquerel discovered that specific materials generated electric current when they were subjected to sunlight. In the year 1877, William Adams and Richard Day learned that selenium materials produced electrically powered currents when subjected to sunlight. In later experiments, the two utilized selenium materials in the production of photovoltaic cells. The cells converted light energy into electricity with an efficiency of 2% (Brownson 12). It took more than a century for the concept to be commercialized. In the year 1955, Bell Laboratory patented a method of generating power using sunlight rays with the help of silicon-based materials. Ever since then, efforts have been directed at the production of more cost-effective, efficient, and reliable solar panels. Modern technologies associated with the source of energy include solar photovoltaic, solar thermal electricity, solar heating, solar architecture, and artificial photosynthesis (Soga 43). Solar energy technologies are either passive or active, and they all aim at providing clean, safe, and renewable electricity.
Step 2
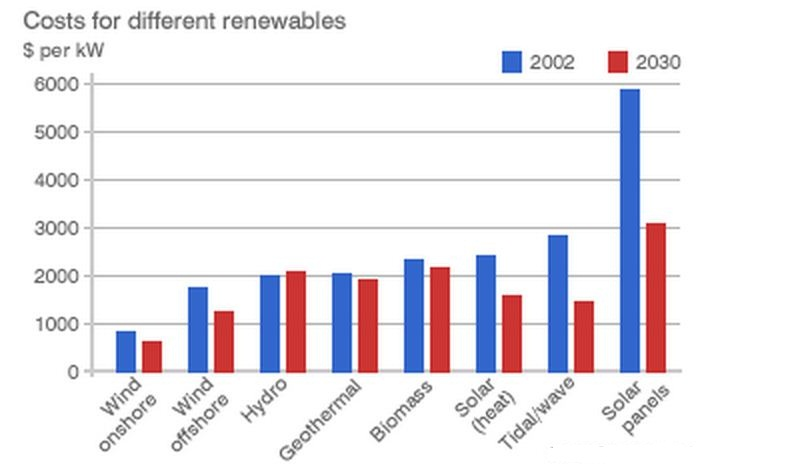
The above graph illustrates the cost and usage of solar energy with respect to other sources of energy. Compared with other renewable sources of energy, figure 1 indicates that solar energy is the most expensive. The graphs indicated above have related patterns of behavior. Compared with other sources of renewable energy, the charts show that the use of solar power is still very expensive. However, the figure illustrates that soon the use of solar energy will be competitive.
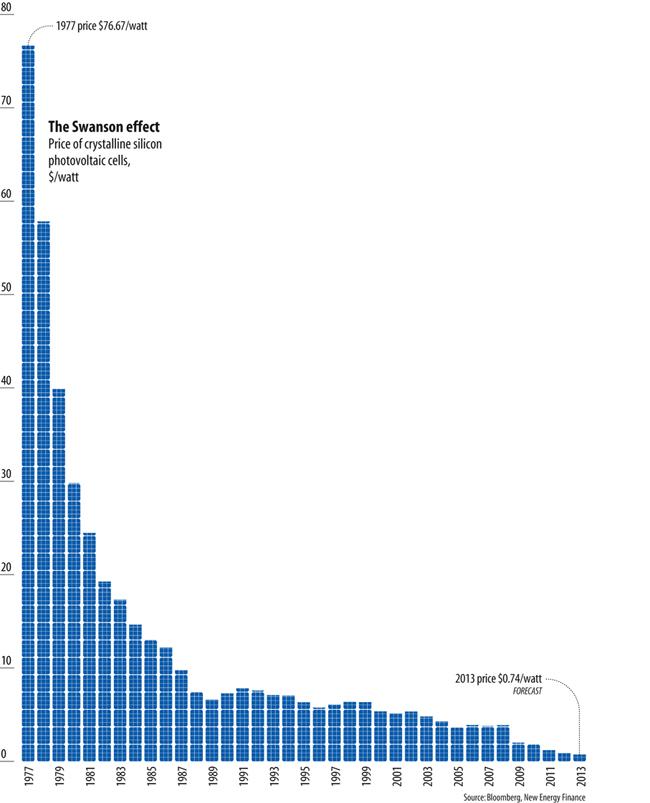
Figure 2 illustrates that the cost of solar energy has been reducing over time. By the year 2013, the cost of solar energy had reduced more than a hundred times as compared with the year 1977. With the development of more efficient technologies, the efficiency of solar energy has increased progressively. The technologies have made it possible for the use solar power to be adopted in light scale industries. The graph indicates soon the cost of solar energy is expected to drop as it has done in the past. The major barriers currently undermining the uptake of solar power are cost, reliability, lack of stable PV policy, environmental issues, lack of skilled labor, and an absence of technical standards.
The cost of producing solar energy is considered a major problem. Electricity from using solar panels is four times more expensive compared with generating electricity with hydro sources. As such, solar technology is still very costly compared with other technologies utilized in the production of power. Solar panels use expensive semiconductor cells to produce electricity from sunlight. The semiconductor materials are built in sophisticated factories that are very expensive to construct and maintain. Equally, the efficiency of solar energy ranges from 20% to 22%. The above figure illustrates that much of the energy received on the surface of the solar panels are wasted.
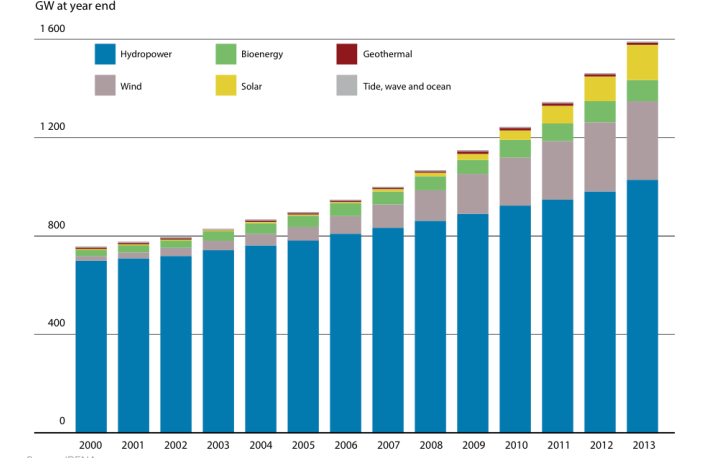
Figure 3 indicates global cumulative installed power production capacity. The graph illustrates that hydro is the most preferred source of power. Notably, the growth of hydropower plants is the least compared with the growth of solar power plants. The use of wind energy and solar energy has increased steadily from the year 2000 to the year 2013. If more than one person were involved in the analysis of the above graphs, a mutual sense of the story could have been provoked because the trend in the usage of solar energy has been consistent.
Step 3
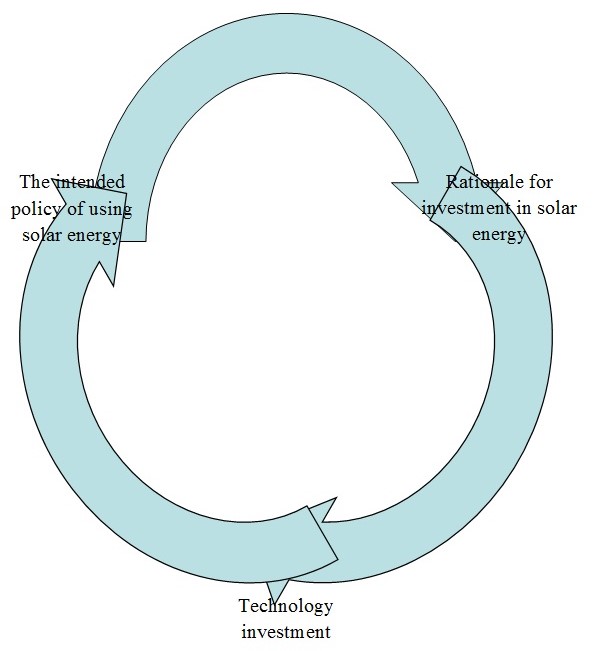
The primary goal of this system is to solve the problems related to the use of solar energy. The system indicates that the issues associated with the use of solar energy rely on technology investment and the intended policy of using solar energy. The mentioned system begins at the rationale for investment in solar energy and terminates at the planned policy of using solar power (California State University 1). Technology investment should be changed to enhance the much-needed technologies required to improve the efficiency of the solar panels.
Step 4
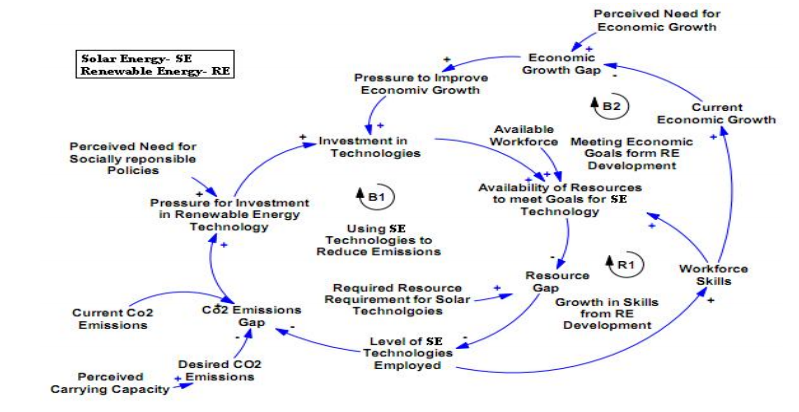
As indicated in step four, there are three elements changing in the causal loop. The elements are the rationale for investment in solar energy, technology investment, and the intended policy of using solar energy. The first element in the loop is B1. The feature illustrates the need to adopt the use of solar energy to reduce the effects of carbon emissions. The second component illustrated is B2. The element represents the financial justification for investment in solar energy. The third component is solar technology investments. As such, the element closes the loop created by the first and the second component.
Presently, the elements are changing in value. As such, the elements are going up the scale. B1 has increased due to the need to lower the effects of global warming. As a result, B2 has also increased. With the increasing cost of fossil sources of energy, more emphasis has been focused on renewable sources of energy such as solar energy (Hahn 57). The increase in B1 and B2 has led to an increase in R1. The above imply that solar power technology investment has a second order impact (Meadows & Diana 67). The investment has enhanced skill levels among the laborers improving solar power technologies. Through this, the need to reduce global warming effects has been attained.
Step 5
The loops illustrated above are balancing loops. Together the loops move the system towards stability. For instance, policies should always be reviewed. Failure to review them will lead to a drop in skill growth. The above will compromise on the growth of technology. With a decrease in technology growth, investors will shy away from investing in solar energy. When all factors are balanced, the system will be stable.
Step 6
Step two generated graphs indicating the capacity of solar energy in the past and its expected growth in the future. The charts illustrated that soon the use of solar energy will be competitive.
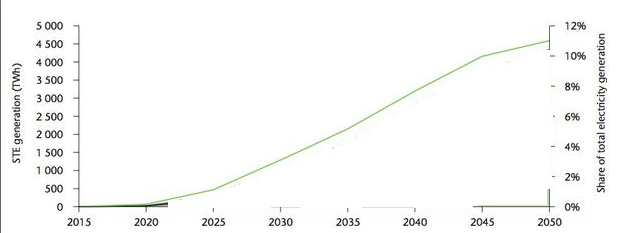
The results from the above model illustrated that the ability of solar energy will increase in the future as speculated in step two. The major barriers currently undermining the uptake of solar power are cost, reliability, lack of stable PV policy, environmental issues, lack of skilled labor, and an absence of technical standards. Solar energy has not been popular in industrial applications owing to the above challenges. Industry owners do not prefer the use of solar energy because they are unreliable and are subject to weather conditions. The technology has been used mainly for domestic home consumption. Tenants utilize solar energy as a supplemental source of energy. Researchers believe that with more studies being undertaken in solar technology more efficient and reliable solar panels may be developed soon.
Step 7
Based on the causal loop, it is apparent that the system has leverage-points that may lead to undesirable penalties. Policymaking is a major point that influences the results of the system. Failure to come up with appropriate policies will result in a drop in skill growth. Following this, a slow growth in technology will be witnessed. With a decrease in technology growth, investors will avoid investing in solar energy. Slow down by the investors will negatively affect the solar industry. Therefore, policymakers should come up with appropriate policies to boost the uptake of solar technologies. Through this, the industry will experience skill and technology growth. In the end, more investors will invest in the sector.
In conclusion, it should be noted that the primary problem with solar power that has discouraged its use is the fact that its technology is still very expensive and unreliable. Compared with other sources of energy, the use of solar power has not been widely embraced. The popularity of solar energy is still lower because its technology is still uncompetitive. In the future, the above issues will be addressed to increase the uptake of solar energy.
Works Cited
Armentrout, David. Solar energy. Vero Beach, Fla.: Rourke Pub., 2009. Print.
Brownson, Jeffrey. Solar Energy Conversion Systems. Oxford: Academic, 2014. Print.
California State University. Sustainability Systems. 2015. Web.
Hahn, Federico. “Self-Powered Instrumentation Equipment and Machinery Using Solar Panels.”Solar Collectors and Panels, Theory and Applications 12.3 (2010). 56-59. Print.
Meadows, Donella, and Diana Wright. Thinking in Systems: A Primer. White River Junction, Vt.: Chelsea Green Pub., 2008. Print.
Soga, Tetsuo. Nanostructured materials for solar energy conversion. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2006. Print.
