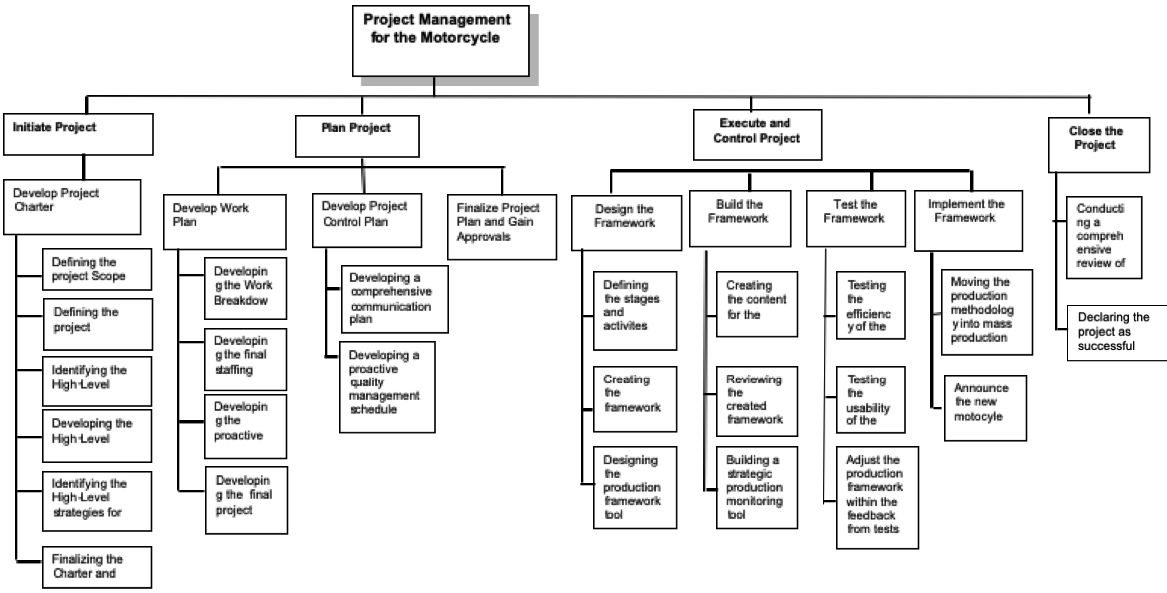
Project management plan
Project planning divides activity into four key areas which are “setting objectives, identifying deliverables, planning the schedule and making supporting plans. Supporting plan may include communication methods, human resources, and risk management” (Drive Your Success, 2011, p. 21). There should be a proper time management framework for project activities. This will ensure success during execution. The project plan outlines activities that have to be carried out to ensure completion of the project. It also shows the other activities which need to be carried out alongside the main activities. The critical path is the path taken by the main activities in the chart. Activities which fall along the critical path must be executed within the allocated time. However, regardless of how well a projected is well managed or evaluated, delays are inevitable. Such delays may arise from a number of factors such as sudden snow fall and delays in delivery of suppliers among others. Causes of delays should be addressed as soon as possible. This will help in avoiding further delays.
Scope of the project
Based on the market research conducted, it was found out that the current product line concentrate on production of middleweight motorcycles are limited to companies operating motorcycle touring businesses. The touring class motorcycles need a project-driven organizational structure that centers on the individual project and customer demands. This approach brings many benefits, including being responsive to the changing needs of the customers, effective at incorporating diverse skills in a team, and useful in project risk management (Gray & Larson, 2011).
Project Goals and Objectives
Project Deliverables
This project shall be carried out in stages and shall involve various output deliverables. These shall include the use of Gantt charts, cash flows, and network diagrams to show the relationship between the various activities involved in the project and generation of resource sheets to display the utilization of the various resources at every stage of the project. In the context of this project, the Gantt chart shall be highly useful in displaying all the project activities and deliverables, their completion dates, and their progress. This is crucial, especially for managing the progress of the project and ensuring that everything is executed as per the plan (Microsoft Corporation, 2012).
Human resource requirement
Team-building strategies
Training approach
The training approach will be done through series of meeting between the internal and external suppliers of project requirements. Training will be continuous depending on the needs and dynamics of the project. Training has the advantage of improving the technical skills needed for the accomplishment of the project.
Rewards
There will be a reward to internal suppliers for a accomplishing each milestone within the set time. The reward will be in the form of monetary allowances and a certificate of competency. The reward strategy has the advantage of ensuring optimal performance and efficiency since it is a motivational factor.
Project Communication
The project directors hold the key to the future of the project. They have a mental picture and a vision of how they want the company to become after a given period of time. Members of the project workforce will be made to feel as being an integral aspect in the implementation of the proposed project. If properly communicated to, they are the strengths that ensure the success of the new procedures.
Technical support to team members
The plan will be communicated through face to face meetings and official emails. The progress will be communicated after every three days. The proposed technical support plan will be monitored every day during the first month to ensure that all the team members are comfortable and motivated. Technical support has the advantage of ensuring that the team members are well equipped and capable of delivering different elements of the heavyweight motorcycle project.
Role of project manager
Characteristics of a project manager within the project
Visionary leadership
The project manager should have visionary leadership skills in order to be competent in planning and deliberation of duties. Besides, the project manager should be organized and goal oriented leader who is keen on transactional discourse of the project. Moreover, the project manager has to be an effective team player who can delegate duties to different parties in the project conceptualization. The visionary leadership will ensure that the project stages are proactively integrated for smooth transition from one stage to another (Wren, 2007).
Transformational management skills
The project manager should have transformational management characteristics such as diversity management and development of an insight that accommodates application of task oriented supervision in line with the project’s demands. Despite task orientation being rated as a high self leadership assessment strategy, action planning is of essence in creating solution oriented task and strategy implementation session for quantifying task orientation levels that are required in the success of this project (Wren, 2007).
Technical skills
The project manager should have technical skills, preferably in project execution to ensure that the balance between the technical and management needs are balanced in the project execution. In relation to the motorcycle project, the project manager will apply this skill in the execution and success evaluation stages in managing the motorcycle project (Wren, 2007).
Project Critical Path
The critical path is important in actualizing the project life and making projections in terms of time involved in each stage of the motorcycle project. From the high level activity precedence table created by the management of the project, the precedence network drawn below was derived.
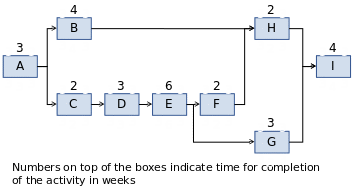
In order to determine the critical path, calculations will be done for the duration of each stage of the project as indicated below.
- Path 1: A → B → H → I = 3 + 4 + 2 + 4 = 13 weeks
- Path 2: A → C → D → E → F → H → I = 3 + 2 + 3 + 6 + 2 + 2 + 4 = 22 weeks
- Path 3: A → C → D → E → G → I = 3 + 2 + 3 + 6 + 3 + 4 = 21 weeks
Apparently, Path 2 becomes the critical path since it is the longest. Path 3’s float is 1 week while that of Path 1 is 9 weeks. This is presented in the diagram below where Path 2 (critical path) is highlighted.
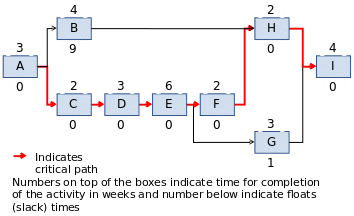
In order to establish the late start-late finish, and early start-early finish, the network is subjected through a critical backward and forward pass as indicated in the diagram below.
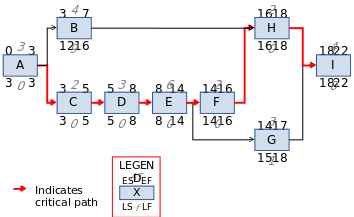
The diagram confirms Path 2 as was previously decided to be the critical path of the project.
Work Breakdown Structure, Pricing, and Costing
Project scheduling, estimating, and cost controls are the main factors of a project management system. For companies engaged in future construction, the right forecast of the future project cost is very significant. There are four criteria of scheduling and cost control, namely, directing progress, directing actions, controlling results, and conserving resources (Wren, 2007).
Project schedule and cost control procedures are very important for the motorcycle project. If one of them is changed, the other will automatically have to change. Even though while formulating the procedures great care is taken that all the related aspects are considered, it sometimes happens that some particular situation is not mentioned in the procedures. In such situations, the concerned engineers or contractors cannot change the procedure at their will. They have to make a formal written request to the concerned project manager, who in turn consults the management. Once the management approves the changes, the same are notified to the concerned parties (Snyder, 2009).
Assigning resources
In the motorcycle project as earlier discussed in the project critical path, step B falls on the critical path while step C and D does not. All the three steps are at a risk of being delayed. As a priority, a project manager should first consider a possibility of continuing with other non critical path activities. This is possible when there are delays affecting critical path activities (Snyder, 2009). This will help reduce the overall impact of delay on the project. In this scenario, since the delay will affect both critical and non critical activities, the project manager should allocate available resources to the critical step, that is, step B (Drive Your Success, 2011). This is because delaying any activity along the critical path delays the whole project. Therefore, all critical path activities should be completed within the scheduled time. Thereafter, resources can be allocated to the non critical path activities. In this scenario, once the critical path activity has been completed, the project manager can then allocate resources to step C first then D because step C comes before step D.
The Gantt project chart
Reflectively, the Gantt project is a success measuring tool for cross platform review of the entire procedures and stages of project implementation. This tool has an application which monitors resources of the project, time allocation and completion tracking. Since it is flexible in creating project tracking charts, this tool is necessary in communication and promotion of the project deliverable variables since it classify each according to the stages, timeframe, and milestones (Snyder, 2009). In implementing this project effectiveness tracking tool, soft skills come in at the point of relevance and procedural adjustments that might be needed following the series of project management dynamics. Specifically, this tool is relevant in the motorcycle project environment in tracking and managing time frame allocated for each project milestone since it can be modified to address changes that might occur in each stage of project management (Wren, 2007). This is summarized in the appendix 1.
References
Drive Your Success (2011). PERT Project Management: Mid-Project PERT Correction. Web.
Gray, C.F., & Larson, E.W. (2011). Project management: The managerial process. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Microsoft Corporation (2012). Manage your project’s critical path. Web.
Snyder, C. (2009). A project manager’s book of forms: A companion to the PMBOK guide, fourth edition. Hoboken, ST: Wiley.
Wren, A. (2007). The project management A-Z: a compendium of project management techniques. USA: Gower Publishing Companies.
Appendix 1: Project Gantt Chart