Introduction
Innovation and Start-Ups Company Broad Concept
Innovation plays a pivotal role in changing the business set-up, especially with the vast spread of internet. In the current contemporary global business landscape, defining innovation has an ambiguous framing as the world needs critically and accurately assessing them in an integral way when defining innovation. The ability to develop and apply new ideas to certain issues by transforming them to new solution that add value to the business. One way innovation can impact positively societies is for development of start-up business. These start-ups innovations epitomise risk taking idea and responsibilities with the objective of developing accurate business models that will meet the market requirements. Additionally, assessing thoroughly the potential to develop enterprise as well as unearthing opportunities that other investors cannot foresee. The fast disrupted pace ideas is becoming a challenging and competitive for the start-up business.
The set-up of start-up venture is undergoing a rapid globalization period, which is making communities to be exposed to more than one term of ideas exchange and design for the solutions. These companies enter the market without the ability to match the technological demands: Despite their efforts, start-up companies fit best in developing economies with the goal of lowering poverty and generating wealth through innovation. The commercial, social, political and legal set up of these country bases on these critical determinant to drive changes. Developing demands and needs of individual will boost start-up culture that is efficient, valuable and inclusive for all stakeholders. Existing firms are using more effective manufacturing methods to improve margins and decrease costs. Others, through competition, also win market share, delivering new goods and services to customers, which are more valuable than their rivals (Canada statistics, 2021). If firms want to raise profitability by increasing costs, they are likely to lose consumers or gain new rivals who see the chance to enter the markets profitably. Many core components build a competitive environment: low entry barriers; low cost of consumer switching; full and reliable information; and an abundance of efficient competition (Kim, et, al., 2020).
Background
Currently, technological growth is moving faster, meaning, every business ventures must depend on this development to meet the market demands. The use of social media platforms, mobile based interaction applications and robots to produce high quality products that befit the quality in the market. According to the recent statistics, there are about 260 start-up companies in Canada every day, which makes it 95000 companies annually (Lagoy and Nguyen, 2019). Covid-19 pandemic has impacted on this growth, as more companies are closing up their activities. This pandemic is a great test for business, especially the new ones, who must improvise ways to get a sizeable share of the market. Those companies that do not incorporate innovative ideas and technology end up closing shop due to low revenue generation. For instance, 801940 were active as of February 2020, this number dropped to 689,900 by in May (Walpole and Isdale, 2020). The strict measure set up by the government to limit movement of people made businesses lose clients, especially the lockdown of some areas.
Corona virus pandemic is not the main reason these start-up firms have been failing. Actually, during the pre-pandemic period (years before 2020), 95% of new business have been failing every year. Experts say “Ran out of Cash” and “No Market Need” are the main reasons these business stopped operating (Walpole and Isdale, 2020). For instance, a good portion of these business were selling products that no one wants. Lack of creativity is the key reason why they cannot develop a reliable customer base which is associated with lack of proper technological background from these business. Technology and innovation has a vast range of ways business can use to look attractive even in the most competitive market bases. Those start-up companies that use these unique ways survive in the first-difficult phase of their existence. Many people start business or consultant services without getting proper knowledge of the customer base, as they are too excited. It is important to have prior information of the technological demands of the market, and ways to beat the existing ones. Lastly, developed business have established a milestone in technological investment that these armature companies cannot meet. Those entrepreneurs who use unique ways are the only ones who successfully survives in the giant-companies dominated market (Gerrans, Pitt and Treepongkaruna, 2017).
Need for use of Innovation and Technology
Internal and external driving forces for small business
Entering a new market demands a lot of care and knowledge to become successful. It is important for the new company to have the right framework to become successful. It is important for them to have the following internal driving forces to run effectively.
- Low customer base
- High number of competitors who are established
- Testing new product
- Limited finances
- Implementing new ideas that haven’t been tested.
- The possibility of having a low customer base
- There is low customer-client trust
- High cost of operation and management
- Possibility of loses.
- Working with inexperienced team and staff due to limited wage limit
- Use the latest technology and innovation
- Heavy wages
- Expensive technology
Without a doubt, these driving forces are the main force new companies must cope up with to remain relevant. Lack of proper strategy will make them run out of business and loss the new clients they had gotten
Power of the forces
These forces should not be taken for granted as they will eventually impact on the stability of the new business. Proper incorporation of technology and innovation will help these business use better ways that will be cheaper and efficient. For instance, offering online delivery services will attract many people to order the goods. The research sample will include two categories. The first category is information from the peer-reviewed literature (Snyder 2019). In particular, it will provide the researcher with data on the most effective technological innovations used by businesses. It is assumed that at least twenty peer-reviewed sources will be analyzed. The second category will be case studies from real companies. The researcher is expected to gain insights into the technologies that have enabled startups to be successful. The sample will include case studies from five companies from different fields of activity. A barrier to data collection is the lack of a sufficient number of cases from start-up businesses; therefore, the sample will be severely limited.
The currency of the research
The modern business area is developing rapidly. Almost every day, there are many new projects that have significant prospects. However, new businesses often face many challenges that lead them to ruin, and in some cases, the reason for the failure may relate to insufficient use of technology drivers. In this regard, research that identifies new drivers for start-ups and focuses on technological and innovative aspects is highly relevant. In this regard, this work will help fill the literature gap and shed light on the relationship between the introduction of digital technologies in a business and its success, which will be useful for entrepreneurs and can provide them with additional tools to improve performance.
The theoretical context
Technology diversify the market base for the business, with the introduction of the new ideas. Technological deficiency is impacting negatively new businesses, as they doesn’t have way to meet customer satisfaction which is avital aspect of a business. Using the right framework and model will improve the chances of survival for the business. Adopting the theory of diffusion allows companies to innovate consumer products and adoption of the right process and the right organizational type. Consumer market are unique and have led to unique different production in as the nature of the goods and innovation must be relevant to the consumers’ needs who have a limited budget. Failure to produce quality products makes these companies to inquire losses as a result of material waste. Managing the resource is essential for the growth of business, it is important to ensure the resource is used well to make profit.
Value of the research
The research findings of this study are expected to provide answers to relevant questions. In particular, the results and conclusions of the work can shed light on the technological incentives that support start-ups and reduce their level of risk, identify the best strategies and requirements for technological competence and education, and prove the importance of technological innovation for business success. In this regard, the research can be seen as a guide that start-up companies will use to ensure their success in the market.
Technological innovation in new business
Technology and innovation is defined as a concept of introducing an existing idea or process which unique technological feature that are significantly different from the existing one. It also involves introducing a new product that will meet more than one demands of the market. Ross, Beath and Mocker (2019), in their book, elaborate on the impact of digital technology on business performance and productivity. In addition, the literature contains much information about why start-ups often fail. For example, Feinleib (2012), in his book, describes many factors leading to failure, including the inability to create a valuable product, loss of money in sales, accounting and investment failures.
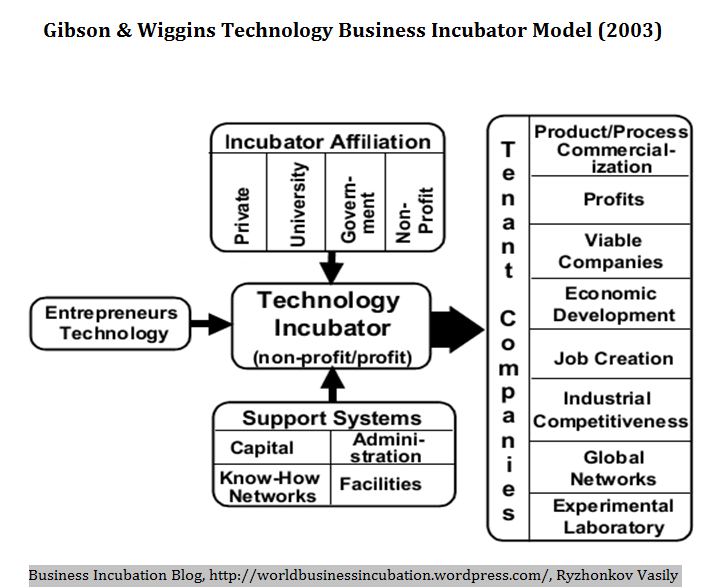
The start of the business is one of the most critical part of its existence. It is during that time business must implement the Gibson & Wiggins Technology Business Incubator model to cautions their activities against the hard times. Many business fail due lack of enough protecting from the limited resource. During that time the business must be handled with care to safeguard the limited resource. Use of incubator affiliation will reduce the overall operational cost that the business will incur. It is vital to introduce unique products that will be supported by bigger organizations.
Research Aim
The aim of the study is to explore what challenges start-up’s face and how digital technologies can improve their success and help reduce risks. In addition, it is essential to draw up recommendations for new business owners, including listing the benefits and consequences of technology and innovation.
Research Questions
The research is designed to answer start-up business failure following questions:
- What are the challenges startups face? Do these problems relate to the lack of using digital technologies?
- What impact does digital technology have on businesses, and how can it contribute to success?
- What impact can technology drivers have on startups, and which ones can be considered the most successful?
Research Objectives
- Review the existing literature to identify technology drivers in the business.
- Explore the challenges that startups face.
- Explore real-world examples of how technology is used to mitigate new business risks and improve business success.
- Identify the best technology practices that contribute to the promotion and success of startups.
Summary
Most start-up companies lack proper technological ideas that would boost their reputation in the market. Today, digital technology and innovation are seen as effective tools that help to advance businesses of all sizes (Gupta 2016). Accordingly, companies often use them to strengthen their competitive advantage, promote new ideas, and achieve success quickly. However, this topic is mainly considered in the context of large businesses that have been present on the market for several years, or the development of entrepreneurship through using digital technologies. Inability to create a valuable product, loss of money in sales, accounting and investment failures. Considerable attention is also paid to the problems of technology start-ups that face barriers to IT governance or organizational problems (da Silva et al., 2015; Giardino, Wang and Abrahamsson, 2014). In this regard, previous studies either address the relevance of digital technologies in a general business context or consider start-ups’ problems as a separate topic that does not relate to digital technologies.
Literature review
introduction
Technology has altered the manner in which organizations direct business by empowering independent ventures to make everything fair with bigger associations. Private ventures utilize a variety of tech – everything from workers to cell phones – to create upper hands in the financial commercial centre. Entrepreneurs ought to consider executing innovation in their arranging interaction for smoothed out combination and to account for future extension. This permits proprietors to make activities utilizing the best technologies available. This literature review will use a compilation of the literature review was carried out by using scientific databases and search engines, such as Google Scholar, Scopus, Web of Science, and some others. Attention was paid to more recent sources, with the exception of the literature on theoretical foundations. The search used keywords that identified resources that would help uncover research questions and deepen understanding of the topic.
Theories related new business and technology
In this study, the theoretical foundation is the entrepreneurship theory that emphasizes the relevance of the research and explains the need for businesses to turn to new technology tools in order to improve their success. These economists believed that the entrepreneur’s function was to implement a rational combination of production factors (capital, land, and labor) and generate a normal entrepreneurial income (Boutillier and Uzunidis 2016). According to Schumpeter, an economic system is capable of self-development only when it contains more than just the interaction of rational combinations of production factors, as it followed from Say’s concept of entrepreneurship. Continuous reproduction of new combinations of such factors is necessary. For example, he believed that new combinations included the production of a good unknown to consumers, or the creation of a new quality of a known good; the introduction of new methods of reproduction, that is, innovations in the production process or commercial use of goods; development of new markets or new market segments; finding new sources of raw materials; introduction of new methods of work organization, and so on. In this regard, the researcher identified the underlying factors that contributed to the growth of entrepreneurial success. The listed determinants can be considered in the context of their linkage to the technological capabilities of a business since modern digital technologies largely support them. Consequently, the theory of entrepreneurship once again emphasizes that the goal of every business, including start-ups, is to achieve success as quickly as possible by using various tool.
Theory of reasonable action
The Reasoned Action Theory is used to describe and forecast comportment based on behaviours, norms and purposes. The structure of the TRA is component: behavioural convictions, behavioural results assessments that lead to mind-set, then normative convictions and inspiration that leads to arbitrary standards. Both the mood and the subjective norm correspond to the decision to conduct the behaviour. This theory relies on a behavioural mind-set in comparison to subjective standards of individuals that may control and possibly influence certain behaviours and have a better sense of behavioural motives (Al Zabi, 2013). Theory of reasoned action is the perceptibility of convictions dependent on parents, relatives, partners, associates and colleagues influences subjective regulations. This plays an important role in the way people interpret actions and opinions.
Small and starting businesses can use this theory to forecast how their potential customer may or may not comply with their pre-existing behaviours and conduction intentions to make decisions of whether to buy the products or not. The choice of a customer on whether to buy or not to buy a specific product depends on the results that the individual expects from the activity after buying the product. If the customers have a negative attitude towards the provided products then their behaviour is as well negative and are most likely boycott the products (Lai, 2017). Conversely, a positive attitude of the customer towards a product provided by a new business would lead to a good behaviour hence the customer the goods. Therefore, starting business are likely not attract many customers and as a result collapse because based on the assumptions of this theory, consumers would not have developed any attitude towards the products that can lead to a purchasing behaviour. Additionally, the theory stipulates that customers’ behaviours relies on the underlying motivation factors. New and starting businesses lack the consumer motivating factors for example the Loyalty program in order to boost their attitude towards these new brands. However, the existence of entrepreneurial advantages affect the personality of consumers and therefore influence their business intentions by making purchases. Nevertheless, entrepreneurship’s drawbacks had little major impact on the customers’ behaviours towards consumption of new products.
Theory of Behaviour
According to the planned behaviours theory, ones conduct majorly depends on three variables, including behaviours, subjective regulations and presumed behavioural influence (Lai, 2017). Small and starting business enterprises are likely to fail and quite the market on the following grounds. New business owners’ action mind-set will influence how likely they are to perform. They are more likely not to do the action because they fear the behaviours would not make difference in life (Fishbein and Aljen, 1995). New entrepreneurs therefore have to find the possibility of a new path for improving business abilities in order to perform better. New businesses are therefore more likely to quit the market if the entrepreneur has it that the business will not do well in the future. The behaviours of starting businesses is likely to influenced in some degree by what other businesses are doing, particularly those in the same industry. Small and starting businesses are therefore more likely to fail because of the actions of the industry leaders they are following. Perceived conduct monitors examine whether people think they have the tools or resources to show their behaviours. Starting business are therefore less likely to do so if their owners believe they are not smart sufficiently to take the required levels of competition. Company behaviour is a product of beliefs, subjective standards and behavioural controls interpreted. It also depends on the company intentions, which managers may consider as their wish to conduct (Sheppard, el, at., 1988). If small and start-up enterprises’ are interested in wide market shares but have not in fact established growth strategies for this. It’s because there’s a market and behaviours difference, then.
Types of innovators in starting business
There are different types of innovators in starting business who have various mechanisms. They have their own strength and weakness while breaking through to a new market. Every entrepreneur must understand the nature of their business to bring out the best out of the business. Those who chose the wrong approach fail as their strategies are not compatible with the latest technology and strategies. The following are examples of innovators in technologically dominated market that affects their efficiencies and rate of success.
Innovators
They are believed to be technological explorers perusing new ideas and findings. Small and starting businesses will find it cumbersome to convince this category of people since they need clear proof and demonstrations of the product(s) launched. Starting businesses can therefore capture the attention of these category and diffuse their innovation by the use of social media and digital marketing which ideally are the information sources of innovators.
Early Adopters
They are considered to be the leading opinion leaders who can exchange constructive feedback on new products or businesses and pursue change and quality regarding new goods and services. According to the Innovation Diffusion Theory, this category requires no convincing when the products/services are open to improvement. Businesses should therefore give instructions for using the product/service to the early adopters.
Early majority
They are followers who read reviews of new items from early adopters before buying the products (Lai, 2017). Starting businesses as well as producers of new products should enhance their social media channels for like YouTube to provide ready information to be fed on by this category. Otherwise, starting businesses may not be successful if they choose a wrong communication channel to diffuse their idea to the early majority.
Late majority
In general, these are sceptics who are not much concerned with improvements in the product. They will therefore adopt a new product only if they feel strongly left behind or missing. It is therefore recommendable that small and starting businesses use marketing documents, facts, opinion leaders’ feedback and case studies to demonstrate how the new products work. However, most of the starting businesses may not successfully diffuse their innovations to this category due to lack of funds and therefore risk collapsing due to lack of customer awareness.
Laggards
According to IDT, customers at this period will only consume from new products in the absence of the traditional substitute goods. This is because, Laggards will come to choose the products long after the other categories have researched and written about the product. This serves a threat to starting businesses as their products will not diffuse into this market segment. The starting and new businesses would have exited the market due to lack of a sufficient customer base before the Laggards category learn about it.
Modern Technological Strategies in New Business
Modern technologies and developed strategic tools should ensure the manageability of organizations in all management levels, such as operational, tactical, and strategic, and, accordingly, the achievement of their goals. In this area, digital technologies play a special role, contributing to the growth of the competitive position of organizations in the market and their general success (Rayna and Striukova 2016). In particular, modern corporate information systems support the intelligent business processes of organizations. In this case, the share of the use of strategic management tools is significant.
Customer Relationship Management
According to the results of a study by the international consulting company Bain & Company, the survey of 10,000 business leaders around the world has shown that most of them actively apply the concept of Customer Relationship Management (CRM), external and internal Benchmarking, and Strategic Planning technologies, solve problems with the involvement of specialized outsourcing and use the Balanced Scorecard system and the TQM concept (Rigby and Bilodeau 2009). In this case, the role of digital technologies is to create positive connections with the target audience, the volume of which is an essential criterion for success. Digital marketing should not be confused with internet marketing. Digital marketing, unlike internet marketing, can apply both online and offline channels. In this case, offline channels include communication terminals, electronic gadgets, and so on, and they can be seen as digital technology drivers for enhancing entrepreneurial success.
Information technology (IT)
Another today’s critical technology driver is information technology (IT). These new technologies, called information innovations in recent years, enable companies to meet their challenges more efficiently (Drnevich and Croson 2013). For businesses, these challenges include improving margins, increasing sales, reducing costs, decreasing risks, and generally stabilizing the market. The purpose of creating and introducing new information technologies is to improve the quality and efficiency of organization management, increase labor productivity, reduce costs for production and management activities, minimize risks, and so on. Those new technologies that allow solving the greatest number of such problems at once are in the greatest demand in the market and bring tangible financial returns to their creators. However, it is necessary to remember that the creation and implementation of new technologies, products, and innovations in the market require investment. In other words, the economic essence of innovation is in the fact that it can generate a lot of revenue, but it also costs a lot to create and disseminate it (Oculus for Business 2020). However, the virtual infrastructure helps to streamline the business processes of many companies, whose management may have significantly more control over their own activities and business development (Janiesch et al. 2020).
First of all, significant savings touch money resources. Resource virtualization technology can reduce the number of high-performance workstations and servers by consolidating them. In this case, digital technologies contribute to significant cost savings for businesses. At the same time, it becomes possible to reduce the number of service personnel members. Virtualization is useful for testing new solutions and training employees in organizations (Janiesch et al. 2020). It can also help reduce infrastructure administration costs, as a key benefit of this technology is the ability to access the management console remotely.
In addition, another plus is the ease of cloning virtual machines. If the organization’s management decides to open an additional office, then it will not be difficult for it to deploy a new infrastructure because the task will boil down to copying images and adjusting software. Of course, virtualization also has a disadvantage: it is necessary to rethink the approach to dealing with system reliability. However, in general, virtualized and cloud environments have opened up new avenues for businesses (Duan, Yan and Vasilakos 2012). The cloud environment implies a model of providing resources, which also helps reduce costs for the company. In this regard, the use of information technology in business is one of the main trends in the life of today’s society. The use of IT in all areas of the economy helps to increase companies’ competitiveness, build new business models, optimize costs, and improve the quality of services for consumers
Summary
The systematization of the variety of types of technologies and innovations creates an opportunity and prerequisites for their more active use by businesses in various fields of activity and contributes to the achievement of a large number of advantages, for example, in the implementation of human talents and ideas, an increase in the science intensity of labor activity, and the introduction of scientific and technical developments. New businesses are therefore more likely to quit the market if the entrepreneur has it that the business will not do well in the future. The behaviors of starting businesses is likely to influenced in some degree by what other businesses are doing, particularly those in the same industry. An economic system is capable of self-development only when it contains more than just the interaction of rational combinations of production factors, as it followed from Say’s concept of entrepreneurship.. The purpose of creating and introducing new information technologies is to improve the quality and efficiency of organization management, increase labor productivity, reduce costs for production and management activities, and minimize risks. In this area, digital technologies play a special role, contributing to the growth of the competitive position of organizations in the market and their general success.
Research Design & Methodology
EthicType and philosophy of research
This work will be based on descriptive research. Descriptive research is conducted to establish and be able to describe the characteristics of the interesting variables in a situation. As part of the research proposal, these variables will be technology and innovation in startups. In this regard, the purpose of descriptive research is to offer the researcher a profile or describe relevant aspects of the phenomenon of interest from an individual, organizational, sectoral, or other point of view. To achieve this goal, the philosophy of research will be a positivist approach. Its essence lies in investigating the phenomenon from an objective point of view and abandoning subjective judgment and interpretation.
Research method
The focus of this study will be on qualitative data. In particular, the qualitative method involves an approach in which data will be obtained through the analysis of text documents and a thematic review (Tobi and Kampen, 2018). This choice is justified by the need to study the individual aspects of the analyzed phenomenon, namely, to determine which technologies and innovations are most suitable for a start-up business as a tool that will ensure its success and effectiveness.
Research design
Qualitative methods and an advanced case study architecture were the analysis style or methodologies used in this case. For example, data from various sources may be used, using qualitative methods, as subject materials for research and referring to exact information. Usually, this data approach or research technique is focused on personal knowledge and findings. However, the Qualitative Approach of Analysis is focused on open methods. In the case study design, knowledge about a particular number of participants using the specific technology and innovation is generally collected. It restricts multiple individuals or test areas and compresses them into a subject that can be correctly studied.
Role of Researcher
In this research, the researcher is mandated to perform the following responsibilities;
- The researcher should seek permission from the relevant sources of information to preserve and defend the liberties and rights of people involved for example copyrights.
- The researcher should ensure that the time frames identified in the research are all adhered to. And if possible, the researcher should crush some research events to minimize time.
- The researcher is to provide both previous impressions and interactions of the subjects, which will allow the viewer or readers to understand the relationship between the researchers and the researcher.
- The researcher may propose and elaborate on the ethical questions that might emerge and will illustrate how to deal with these things in the report.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research
The numbers and estimates used for quantitative analysis are based on the creation of a theory. It builds on the data gathered to confirm an insight and to make a decision. Through this approach, the general facts on the subject can be established and analyzed with accuracy. This technique uses experiments, observations, and other extensive surveys to do a proper study. Quantitative research creates high confidence for the customers who trust the statistics.
In this study, data and facts from previous evaluations will be used to attain the objectives. For example, the customer the use of technology in business operations can be gathered by analyzing statistics and researching data (Tobi and Kampen, 2018). Using different sources, a proper method can be developed to determine the extent of technology and innovations required for use by start-up businesses. The researcher and the start-up business will use the knowledge evaluated to create statistics and take the right steps to strengthen their motivational strategy in their business. Via this study, management will follow suitable methods to raise technological use and innovation management. This analysis would also describe the different ways in which managers will identify and adopt technologies and innovations suitable for the start-up business. A good boss has to inspire his workforce to ensure that they use the most effective technologies and innovations that meet customer demands.
The qualitative approach, on the other hand, is spoken in a proper language. It is used to understand the subjects’ ideas, experiences, and thoughts. Using this technique, data evaluation has been improved for a long time. Many people do not believe in the result of this approach so it can be seen as partial. Under this investigation, the tops are not well understood in detail. This encourages scholars to analyze in their terms what happened to the school. This study is important to develop the best technology strategy to enhance the well-being of team members.
The study would examine conclusions, open-ended questions, literary critiques, and hypotheses obtained from the literature reviews of various scholarly works. This insight would show the suitable and unsuitable technologies and innovations for the start-up business. But the provision of the facts is essential to prevent being it from being biased.
Population and sample size
The population was to be accounted for all the businesses that adopt the new technologies and innovations suitable for start-up businesses. The sample size involved studying those businesses which are not older than two years of operations. This will be sufficient in determining the best technologies and innovations that enhance the sustainability of start-up businesses in operation
The nature of the data
To gain an understanding of the topic and identify technology drivers for startups, this study will focus on previous research that confirms the relevance of technology and innovation for businesses and on case studies from real startups who have shared their success stories. It is expected that in the process of searching for data, the researcher will turn to scholarly databases such as Google Scholar, Scopus, Web of Science, and others. In addition, attention will be paid to reputable news websites and start-ups’ official websites to extract information about the technology used.
Data collection
The research sample will include two categories. The first category is information from peer-reviewed literature. In particular, it will provide the researcher with data on the most effective technological innovations used by businesses. It is assumed that at least twenty peer-reviewed sources will be analyzed. The second category will be case studies from real companies. The researcher is expected to gain insights into the technologies that have enabled startups to be successful. The sample will include case studies from five companies from different fields of activity. A barrier to data collection is the lack of a sufficient number of cases from start-up businesses; therefore, the sample will be severely limited.
Data analysis
Data analysis will be carried out in three stages. In the first step, data from peer-reviewed sources will be examined and categorized by type of technology and business innovations. It will also be necessary to rank them according to their effectiveness. The second stage will involve selecting the technological innovations that startups have used, to compile a list of them (Tobi and Kampen, 2018). The third stage will involve data comparison and analysis. In particular, it will be necessary to determine which innovations are unique and which have already proven their effectiveness, how they have influenced the activities of new companies, and how the startups have benefited from them.
Data collection methods
This research will majorly use data that was obtained from internet sources, literature review of various technological and innovation findings as well as basing on past experiences. Since it is about a start-up business, only data that is relevant within the last two years will be used to build the starting business on the latest business trends and market dynamics. The research sample will include two categories. The first category is information from the peer-reviewed literature (Snyder 2019). In particular, it will provide the researcher with data on the most effective technological innovations used by businesses. It is assumed that at least twenty peer-reviewed sources will be analyzed. The second category will be case studies from real companies. The researcher is expected to gain insights into the technologies that have enabled startups to be successful. The sample will include case studies from five companies from different fields of activity. A barrier to data collection is the lack of a sufficient number of cases from start-up businesses; therefore, the sample will be severely limited.
Combination research
This approach will incorporate both qualitative and quantitative data analysis approaches. This is to ensure a big significance in the value of the data besides allowing the researcher to gain an in-depth understanding of the technological and innovative tools that suit a start-up business (Sileyew, 2019). Qualitative analysis will look into the relevance of technology and innovation tools to individual business situations.
Limitations of the study
A limitation of this study is the fact that it will not include face-to-face interviews with start-up representatives, for safety reasons and because of the difficulty of contacting them. At the same time, obtaining information about personal experience would be able to deepen the research and make its conclusions more accurate.
Reliability and Triangulation
The measurements will be reliable and the research will determine the extent to which they are unbiased and thus provide accurate calculation over time and the different components in the instrument. This is tested for the stability and consistency of the data in the reliability review (Marczyk, 2019). The researcher will verify the accuracy and consistency of the method of calculation in the case of a reliability review. Reliability has many meanings and methods, but the term is consistent in many environments. When reliable findings are produced during data processing, this calculation complies with the reliability criteria.
Ethical issues
Given the fact that the research is theoretical and does not involve communication with people, ethical issues will only relate to reputation and data confidentiality. To resolve these issues, the researcher will use only the data that is available in the public domain. In addition, to protect the reputation, the researcher will avoid making assessment judgments to startups and will be only guided by the relevance of the data. Additionally, this research will ensure and adhere to all the sustainable goals by considering environmental hygiene. In general, this research will acquire its data using legal means and will not accept any unauthorized data.
Project Plan
In this case, the milestones were chosen to highlight the readiness of each phase of the research project. Accordingly, they coincide with the basic tasks that the researcher must perform. The approximate duration was calculated taking into account previous experience in writing research papers and searching for literature. However, in some tasks, the time is increased by one week since the search for literature and company cases can take more time than planned due to the novelty of the topic and the lack of a large amount of information about start-ups’ success. The following will be adopted to develop an assessment of the reasons why technology plays in their failure
Results and findings
For small companies to work every day, they depend on the technologies. The technical advancements affect small businesses across different markets, from notebook computers with web access, to scanners, online file storage, and web-based applications. Technology may have a favourable and unfavorable impact on small businesses, based on the interests of a company, on the goods they want to use, and how employers and workers prepare with new systems. The front end (client-side) and the back-end are the two sides of technological implementations for companies (server-side). On the server-side, for example, the apps will be the operating system, the software server, the database, the web interface, and the programming language. The web framework is placed on the number one of the top one (Wouters, et, al., 2018). These use the Web, while the mobile device uses the native program and the browser runs and maintains HTML, CSS, or Java scripts. The rationale that drives the program is developed for the case of back-end technology. The LAMP stack is some examples of the backend used by startups in the USA (Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP). However, recently, rather than PHP, start-ups and small companies favored programming languages such as Ruby and Python (Rodrik, 2018). In addition, a web application to be written in the above languages is chosen. These implementations are provided with user authentication and access to data resources, thereby preventing developers from creating the application.
For start-ups, the commodity value is typical of a high concern than the techniques making LAMP, Python/Django to be the commonly used. Tech-savvy startups use Java and Scala (with or without GWT), Python (Django, Pylons, Flask), Rails (with and without Ruby Frameworks), LAMP (with or without MVC Frames), and NodeJS throughout the front end system (Rodrik, 2018). In the background of the start-up market, the appropriate technologies are Erlang, F#, AMPQ, mixing the SQL and NoSQL storage solutions (MongoDBs, Cassandre’s, HBase, MySQL, Postgres, Raven, and Big Table clones among others.
A trend for start-ups is ‘cloud hosting’ like most organizations. It has its advantages because there are no utilities to run or maintain which entails low costs. The use of Cloud Computing for startups has always been more convenient because of the help it offers to host and scale mobile apps by only paying for the services used. AWS, Salesforce, Rackspace, and Microsoft have cloud platforms for startups in the US. Despite its use by large platforms like Linkedln In, Pinterest, NASA, and Dropbox, startups can as well adopt this technology for data storage (Wouters, et, al., 2018). To shield the network from attackers, starters should use cloud technologies. To secure the network, cloud technologies will support startups. It provides security tools to secure personal information. Most cloud services provide their customers with real-time tracking.
Start-ups chose a wide variety of American tools for programming languages. Whereas 81% of start-ups choose JavaScript, 67% have taken Ruby and Python, as Java has made it to 64%. 44% and 42% of startups in its stacks used other smaller language programmers like Perl and PHP. Start-ups consider Ruby on Rails, HTML5, jQuery, CSS, and backbone ideal for use in front-end technology (Rodrik, 2018). Finally, startups using MySQL for storage and databases are 85% and Oracle is embraced by 58% of startups. Additional storages are used by startups, such as Hive (46%), Redis (38%), MongoDB (31%), and Habase, PostgreSQL, and Cassandra (27%) throughout the United States (Canada statistics, 2021). The most appropriate for start-ups led by Soir was considered for the search group Elasticsearch. Many Canadian start-ups use Elasticsearch and recommend it for their search services. Integrations of API − Twilio guidelines, backed by Facebook API and SendGrid. Machine Learning, Big Data, and NLP are advanced technologies used by startups. Finally, Hadoop, Amazon Redshift, and Hive are Big 5.1 Data applications found to be suitable for Startups.
In 2016, Git’s open-source code for flexible version control and security solutions was used by 70 percent of the start-up businesses as a part of the stack. It’s still the most common. JQuery (63%), Jenkins, (430%), Hadoop, Ajax, Prototype and Selenium (27%), Backbone, Node.js, (20%), and spring are the other bookcases used by businesses. Other bookcase services for companies include spring (23 percent). Other startup platforms include Facebook on the workspace, Slack, Yammer, Google applications’ email services, and Office 365, marketing emails via Sendgrid, Mandrill, and Mailchimp, and project management facilitated by Asana (Wouters, et, al., 2018), Wunderlist, and Trello. Other resources used by startups are available in internal communication categories. The other startups in the U.S. and Canada have taken use of Pingdom, Uptime Robot, and Sentry for Wireframe, Prototyping, Hosting, and Monitoring business activities. Through using tools such as Google Analytics and Flurry, startups will perform their analytics well. In the U.S. and Canada by the Freshdesk, Zendesk, and Useresponse customer support and tickets as well as increased distribution of services for a start-up business is used (Kim, et, al., 2020). Another technical problem learned from this study was the customer chat. Many startup companies in the USA and Canada have employed Chatlio and Olark for customer chat and tracking, as well as by buffers and Hootsuite’s social media management. Innovation of Freshbooks and Quickbooks has also been supported by the financial services of start-up companies in the USA
Mobile apps on the iOS platform are more built by startups than on the Android platform. Since is promise higher efficiencies than Android with superior hardware. Most start-ups have preferred, while using the Heroku trailing list, to use the AWS infraction and hosting (Kim, et, al., 2020). The success building of AWS’s global infrastructure. Low latency, low packet loss, and high network quality are offered by AWS regions. The 100 GbE fiber network backbone is fully redundant and also provides several terabits of bandwidth between regions. Heroku, on the other hand, faces buffering, low data protection, and is costly for start-ups.
Under DevOps tools, Startups are mostly pursued under Chef, Ansible, and puppet. Chef offers fast IT automation to automate the web-scale IT that is scalable and versatile. Chef is also a configuration administration tool such as Puppet, using ‘recipes” as web application configuration manuals, servers, and load balancers. The Chef’s recetas describe the technology components and how they can be deployed, optimized, and handled (Canada statistics, 2021). This schedule demonstrates how any Chef code is created, tested, and deployed. Chef’s settings policy enables users to identify infrastructure as code. Its deployment tools will monitor workstations, development networks, and cloud instance configuration changes. Puppet allows consumers in conjunction with detailed documentation and real-time updates to understand and respond to developments taking place in applications (Kim, et, al., 2020). These modifications can be identified and problems fixed by users. Puppet treats the infrastructure as a code that helps to check and test all settings in the construction, testing, and production environment. This puppet includes the Puppet agent daemon that is running on the servers of the client. It has another part called the Puppet Master, which includes the settings for all hosts. The marionettes agent and marionettes master are safely encrypted with SSL. Ansible is a basic but effective server and configuration management platform which can turn an organization’s DevOps by upgrading IT and making applications quicker. It automatically manages setup, orchestrate, and deploys server, clouds, and various other IT specifications.
Ruby on Rails supports start-up in the United States and Canada as rapidly and easily as possible to create any Web application. These models can be built earlier than anticipated to facilitate start-up operations. Twitter, Github, Walmart Labs, Ruby on Rails can be used for digital marketing by start-ups. Django has fewer scripting, versatile applications designed and implemented fast, and is ideal for start-up’s with a particular emphasis on automation. Used for Pinterest and Instagram. Start-ups can also use the Node.js framework to create alternatives in an application that provides the start-ups with a better experience in real-time. NoSQL is also ideal for start-ups as it is used to generate, store, process, and extract vast volumes of data quickly and easily for all applications without causing performance problems. Consequently, this is ideal for improving efficiency. The start-ups are Cassandra and MongoDB, for instance, used in the databases. JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is suitable for use in data exchange between various start-up platforms. Data can be regulated, maneuverer, modified, or blended between applications.
On average, 96,000 new enterprises joined the country’s economy last year, accounting for about 9.4% of all Canadian businesses (annual birth rates). Accommodation and food facilities were the highest birth rates. Higher birth rates for industries continued to be lower for 5-10 years. 63% of Canada’s small businesses lived for five years and 43% lasted 10 years due to government subsidies and start-up tax vacations (Canada, 2021). The company’s incoming survival rate increased steadily and gradually from 2002 to 2014. In the hosting and food services market, the lowest survival rates were. Companies have greater rates of survival when born bigger. In the first three years, 23% of workers with 1–4 employees failed and only about 14% with 20–99 employees failed. In 10 years, over 57% of new companies employing 1–4 workers failed, but in 10 years fewer than 50% of firms employing over 20 employees failed.
New firms’ survival rate in Canada
Solid survival rates can be seen as markers of competitive overall health. This research measured survival rates for 13 cohorts of new companies, which were set up inclusively between 2002 and 2014. In the first year, on average 98% of new companies survived, after five years, 63% survived and just 43% survived after ten years. In cohorts of new companies formed between 2002 and 2014, the trend of survival rates was shown to be largely consistent. In three years since their birth, new company cohort deaths had been at the peak level and the survival rate marginally declined in subsequent years (Mullins, 2017). A cohort review shows a stable, incremental rise in firm incoming survival rates over the observation period, except for a small decrease in the 2009 firm incoming cohort. In the 2002 and 2011 cohorts, the three-year survival rates were 75% and 82% respectively. Similarly, the mortality rate for the cohorts in 2002 and 2007 was 53% and 55% respectively for 2002 and 2007 (Canada, 2021).
The increase in survival levels of new business in Canada could be due to two reasons. First, the automation of many unqualified activities has helped start-ups to replace entirely machine production lines. This cut prices for suppliers, dealers, supermarkets, and several other companies. On the flip side, it may not be so good for job hunting companies to gradually expand employment automation (Mullins, 2017). Secondly, global internet access has undoubtedly been increasing throughout recent years. There is a much bigger market with new businesses who communicate to their clients using the Internet. On the flip side, though, a global increase in Internet access can lead to a decrease in demand in conventional means of communication, which for others is a bad result — telephone service providers need to change their offers to remain competitive because paper and incoming printers could be seeing less revenue.
Birth Rates by Industry
The services industry showed higher birth rates than the goods industry during the observational period from 2002 to 2018 consistent with earlier results (Macdonald 2012). This may be demonstrated by reduced entry rates, fewer access constraints, and a greater demand for the Services sector technology and creativity than that for the Goods sector (Canada statistics, 2021). Host and nutritional facilities (12.6%), led by educational, scientific, and technological services ( 11.3%), transport and warehousing (11.3%) as well as knowledge and cultural sectors provide the largest overall birth rates (11.1 percent). Agriculture, fisheries, forestry, and hunting (4.7%) and production accounted for the lowest average birth levels (5.2 percent).
Companies use various tactics to increase their earnings in a dynamic environment. In the Canadian service sector, startups have found their hand to enter the market due to high levels of competition. Existing firms are using more effective manufacturing methods to improve margins and decrease costs. Others, through competition, also win market share, delivering new goods and services to customers, which are more valuable than their rivals (Canada statistics, 2021). If firms want to raise profitability by increasing costs, they are likely to lose consumers or gain new rivals who see the chance to enter the markets profitably. Many core components build a competitive environment: low entry barriers; low cost of consumer switching; full and reliable information; and an abundance of efficient competition (Kim, et, al., 2020). Markets are likely to deviate from competitive results without these factors. Startup businesses, therefore, have to innovatively gain the technological advantage that will suit them to compete fairly in the service industry. For example, they can use advertisements, after-sale services, and customer feedback to foster their relationship with customers and sell off competitively.
In a dynamic and creative marketplace, the competition bureau (Office) guarantees that Canadian enterprises and customers thrive. As an independent law enforcement body, the Board is responsible for the administration and application of the Competition Act, the Consumer Packaging and Labeling Act (except for the food sector), the Textile Labelling Act, and the Precious Metals Marking Act, under the leadership of the Competition Commissioner (Kim, et, al., 2020). The Board is responsible. The basic operational premise of the Board is that both industry and customers are competitive and that regulations can be minimally intrusive to market forces, enabling competition to fuelled growth and enhanced results for Canadians. Startup businesses, therefore, have themselves to defend (Von Briel, et, al., 2018). They have found themselves lagging behind market measures as they suffer from economies of scale and head start gains that are enjoyed by existing firms. Startup firms, therefore, have to adopt cost-minimizing methods of production, enhance efficiency and quality of goods and services for their future sustainability.
After three years, new companies in the product market exhibited higher survival rates than the Services industry. In the goods industry, after 10 years 46% of company entrants remained involved, compared with 42% for the services industry (Canada, 2021). Businesses in the housing, fast food restaurants as well as other services industries showed the lowest survival rates. About 30 percent of enterprise entrants in these two markets struggled within about three years and far less than three among them lasted 10 years. In the technical, science, and technology facilities, and the property and renting and leasing sectors, new businesses were more likely to succeed. Just about 15 percent of companies in these two sectors collapsed within about three years, upwards of half of which have survived for over ten years. Technology and innovation is defined as a concept of introducing an existing idea or process which unique technological feature that are significantly different from the existing one. It also involves introducing a new product that will meet more than one demands of the market. Ross, Beath and Mocker (2019), in their book, elaborate on the impact of digital technology on business performance and productivity. In addition, the literature contains much information about why start-ups often fail. This paper, therefore, summarizes that technologies and innovations applicable in the sectors of real estate, goods, and food are the most suitable for startup businesses in Canada.
Government support
The federal government provides funding for creativity and development through its departments and agencies’ management of the program sources. In 2017, about a fifth of the recipients of this assistance were companies in the industrial sector, which earned almost a third of the overall aid income (Von Briel, et, al., 2018). The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect on jobs and income of recipient undertakings in the manufacturing sector from 2007 to 2017 of federal development and innovation funding (Mullins, 2017). This study shows that federally funded companies have seen higher workforce and sales gains compared to non-profit companies. For the next three years, job increase for recipient companies averaged 1.8% per annum, with companies without funding seeing an overall decrease in employment. The annual average growth in income of beneficiary enterprises during the same time was 4.6 percentage points higher than that of non-beneficiary enterprises.
The Government of Canada’s Innovation and Skills Plan includes investment in clean emerging business technology. The nine initiatives are financed and supported by SDTC, which identifies, finances, and fosters the vital game-change technology in a clean energy economy (Canada, 2021). A team of government-wide experts will advise clean technology firms through the Sustainable growth hub. The hub offers one convenient connection point for renewable energy initiatives and services. Start-up businesses can therefore take advantage of this government support to foster their technological use towards the achievement of sustainable development as outlined in the global vision 2030.
Problems in business technological innovation
Startups have found it difficult to access and measure their levels of technological innovations. This is due to the lack of accuracy was criticized for the popular feedback of innovation indicator, R&D spend for companies (Plant et al. 2016). It has also not shown a clear connection to patenting in Canada in recent years, a typical indicator of the output of the invention phase (Greenspon and Rodrigues 2017). Although patents may also allow the invention to propagate (Gallini 2002), many innovations are not patented. In addition, so-called patent thickets can potentially impede invention (Brander 2010). Consequently, at least in all industries, the relation between patenting and the propagation of invention is also not direct.
Another popular indicator of innovation breadth – science papers – which erupted almost in line with a slowdown in economic growth may also be questioned (Von Briel, et, al., 2018). In reality, in contrast to the publications themselves, citations of scientific articles provide a stronger measure of the impact of a specific piece of science. In short, while we should agree that, if there is smoke, there is a burn, the relationship between many of the measures in these classifications and the objective of raising the living conditions of Canadians is not easy and mechanistic (Canada statistics, 2021). As a result, start-up businesses cannot easily measure and identify new technologies and innovations suitable for their solvency.
Conclusion
The success of start-up companies relies on the level of technological investment that has been put in to help them get a fair share of the market. Covid-19 pandemic has impacted on this growth, as more companies are closing up their activities. This pandemic is a great test for business, especially the new ones, who must improvise ways to get a sizeable share of the market. Those companies that do not incorporate innovative ideas and technology end up closing shop due to low revenue generation. In this regard, previous studies either address the relevance of digital technologies in a general business context or consider startups’ problems as a separate topic that does not relate to digital technologies.
In turn, no direct research that would explain how digital technology can contribute to a startup business’s success has been found. At the same time, it has already been identified that technological innovation contributes to the growth and promotion of new businesses. At the same time, entrepreneurship theories discussed later in this paper emphasize the need for businesses to focus on entrepreneurial income and integrate additional drivers of success into their work activities. Therefore, the basis of the theories in this project includes a combination of basic theoretical positions regarding the determinants of success, concepts that emphasize the need to introduce technological innovation into business, and key aspects of the impact of digital technologies on companies. It’s still the most common. JQuery (63%), Jenkins, (430%), Hadoop, Ajax, Prototype and Selenium (27%), Backbone, Node.js, (20%), and spring are the other bookcases used by businesses. Other bookcase services for companies include spring (23 percent). This shows the level of input many companies fail to give in ensuring their successes.
Accordingly, companies often use them to strengthen their competitive advantage, promote new ideas, and achieve success quickly. However, this topic is mainly considered in the context of large businesses that have been present on the market for several years, or the development of entrepreneurship through using digital technologies. Inability to create a valuable product, loss of money in sales, accounting and investment failures. Considerable attention is also paid to the problems of technology start-ups that face barriers to IT governance or organizational problems. In this regard, previous studies either address the relevance of digital technologies in a general business context or consider start-ups’ problems as a separate topic that does not relate to digital technologies.
Reference List
Al-Zoubi, M. I. (2013). Predicting EBusiness Adoption through Integrating the Constructs of the Rogers’s Diffusion of Innovation Theory Combined with Technology-Organization- Environment Model. International Journal of Advanced Computer Research, 3(4), 63.
Canada statistics. (2021). Canadian New Firms: Birth and Survival Rates over the Period 2002–2014, May 2018 – SME research and statistics. Ic.gc.ca. Web.
Canada, C. (2021). Technology-led innovation and emerging services in the Canadian financial services sector – Competition Bureau Canada. Ic.gc.ca. Web.
Dereli, D., 2015. Innovation Management in Global Competition and Competitive Advantage. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences, 195, pp.1365-1370.
Doğan, E., 2016. The Effect of Innovation on Competitiveness. Ekonometri ve İstatistik Sayı, [online] 24, pp.60-81. Web.
Drnevich, P. and Croson, D., 2013. Information Technology and Business-Level Strategy: Toward an Integrated Theoretical Perspective. MIS Quarterly, 37(2), pp.483-509.
Duan, Q., Yan, Y. and Vasilakos, A., 2012. A Survey on Service-Oriented Network Virtualization toward Convergence of Networking and Cloud Computing. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 9(4), pp.373-392.
Elia, G., Margherita, A. and Passiante, G., 2020. Digital entrepreneurship ecosystem: How digital technologies and collective intelligence are reshaping the entrepreneurial process. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 150, p.119791.
FISHBEIN, M.A. et AJZEN, I. (1975). Belief, attitude, intention and behavior: an introduction to theory and research, Reading, MA, Addison Wesley.
Gerrans, P., Pitt, D. and Treepongkaruna, S., 2017. Milestone Birthdays and Retirement Investment Behaviour. SSRN Electronic Journal,
Greenspon, Jacob, and Erika Rodrigues. 2017. Are Trends in Patenting Reflective of Innovative Activity in Canada? Ottawa: Centre for the Study of Living Standards Research Report 2017-02. April.
Gallini, Nancy T. 2002. “The Economics of Patents: Lessons from Recent U.S. Patent Reform.” Journal of Economic Perspectives. 16(2): 131-54.
Kim, H. J., San Kim, T., & Sohn, S. Y. (2020). Recommendation of startups as technology cooperation candidates from the perspectives of similarity and potential: A deep learning approach. Decision support systems, 130, 113229.
Lai, P. (2017). THE LITERATURE REVIEW OF TECHNOLOGY ADOPTION MODELS AND THEORIES FOR THE NOVELTY TECHNOLOGY. Journal Of Information Systems And Technology Management, 14(1), 21-38.
Lagoy, R. and Nguyen, J., 2019. Start-Up Pavilion: Bringing Together Start-Ups and Established Companies. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 20(4), pp.55-56.
Marczyk, G., 2019. Essentials of Research Design and Methodology.
Mullins, J. (2017). The new business road test: what entrepreneurs and investors should do before launching a lean start-up? Pearson UK.
Oculus for Business, 2020. Bringing Virtual Reality into Your Business. [online] Harvard Business Review. Web.
Osmundsen, K., Iden, J. and Bygstad, B., 2018. Digital Transformation: Drivers, Success Factors, and Implications. In: The 12th Mediterranean Conference on Information Systems (MCIS).
Plant, Charles. 2017. Canada’s Patent Puzzle: Do We Have a Problem with Securing Patents or with the Commercialization of Them? An Impact Brief, Impact Centre, and the University of Toronto.
Rayna, T. and Striukova, L., 2016. Involving Consumers: The Role of Digital Technologies in Promoting ‘Prosumption’ and User Innovation. Journal of the Knowledge Economy.
Sileyew, K.J., 2019. Research design and methodology. In Cyberspace. IntechOpen.
SHEPPARD, B.H., HARTWICK J., & WARSHAW. P.R. (1988). The theory of reasoned action: A meta-analysis of past research with recommendations for modifications and future research. Journal of Consumer Research, Vol. 15, 1988, pp. 325-343.
Tobi, H. and Kampen, J.K., 2018. Research design: the methodology for interdisciplinary research framework. Quality & quantity, 52(3), pp.1209-1225.
Rodrik, D. (2018). New technologies, global value chains, and developing economies (No. w25164). National Bureau of Economic Research.
Von Briel, F., Davidsson, P., & Recker, J. (2018). Digital technologies as external enablers of new venture creation in the IT hardware sector. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 42(1), 47-69.
Walpole, S. and Isdale, W., 2020. Business Interruption Insurance and the COVID-19 Pandemic. SSRN Electronic Journal,.
Wouters, M., Anderson, J. C., & Kirchberger, M. (2018). New-technology startups seeking pilot customers: Crafting a pair of value propositions. California Management Review, 60(4), 101-124.
