Introduction
The contemporary society has been ushered into an era where virtually all people have secured Internet-enabled gadgets that can facilitate their interaction or business operations through social media. Platforms such as Facebook, WhatsApp, Twitter, Flickr, YouTube, and LinkedIn among others have enhanced the manner in which people socialize and market their products or services. Social media has become part of people’s daily living because of the extent to which it has altered virtually everything ranging from communicating, education, conducting business, and socializing.
However, it is crucial to make a cause-effect argument regarding this study’s overall perception of social media in relation to its impact on the individual user, the society, and the global economy. Although social media platforms have boosted financial performance levels among many businesses because of their capacity to help in advertising their products and services internationally to attract a huge customer base, the underlying incapability to control the content exchanged by users has contributed hugely to moral decadence among individual users and, consequently, the society.
However, because of the uncontrolled exposure to unrefined contents, especially among children and teenagers who are social media platforms’ biggest consumers, this paper recommends the need for parents to not only closely monitor what these groups of people engage in on a daily basis but also discard accessible applications that do not promote constructive and educative agendas.
Pros of Social Media
One of the sectors that have significantly benefited from the advent of social media platforms is business. The study by Garrido-Moreno and Lockett presents the tourism industry as among areas that have recorded huge transformations in terms of the manner of promoting their services, interacting with clients, and, consequently, performance (172).
Major Internet-facilitated tools such as Facebook, WhatsApp, Instagram, and YouTube among others have been linked to substantial benefits in the tourism and hotel businesses, including enhancing brand image, augmenting e-word-of-mouth, and boosting clients’ awareness and capacity to get prompt feedback regarding various services or products on offer (Garrido-Moreno and Lockett 172). From this finding, social media is depicted as helping to improve the value of businesses operating in the tourism sector.
It is crucial to examine the role that social media has played in augmenting organizations’ human resource management departments’ operations. Olivas-Lujan and Bondarouk believe that the deployment of various Internet-enabled platforms such as LinkedIn has been fruitful to many organizations not only in the U.S. but also across the world. These authors reveal a shift from the conventional perception of social media platforms as involving tools that are only meant for socialization to the appreciation of their contribution to enhancing business performance. In America, approximately 90% of all renowned corporations such as Google, Facebook, and General Motors among others deploy social media to boost their HRMs’ operations, including recruiting, selecting, managing, and engaging their employees (Olivas-Lujan and Bondarouk 11).
Conventionally, companies could only communicate to a few people, especially when in need of new workers. As a result, the limited number of accessible potential candidates compromised issues such as diversity and multiculturalism, which have been tested and proven effective in boosting organizational performance and, consequently, profitability (Baum and Kabst 353).
The initial step that a company that is seeking new employees engages in entails passing the message to people regarding its desire to have particular positions occupied. Currently, the advent of social media such as LinkedIn and Facebook has enabled such businesses to reach the maximum number of interested candidates from all over the world. Bearing in mind that many organizations have subsidiaries that are spread across different regions around the globe, deploying the above social media tools has the potential of satisfying their recruitment needs.
A study by Baum and Kabst presents Internet-facilitated platforms as effective in augmenting conventional employee recruitment and selection frameworks (356). In particular, as presented in Figure 1 below, utilizing social media has allowed organizations’ HRM to reach an unlimited pool of potential recruits from all regions across the world.
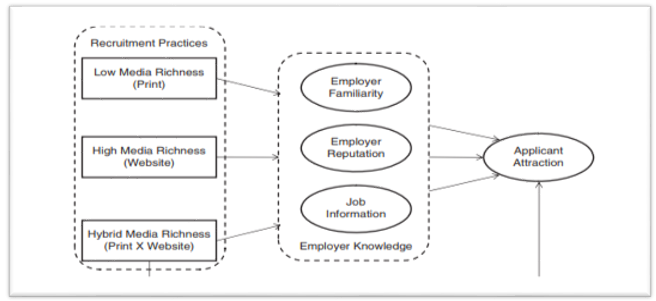
The book by Bondarouk and Olivas-Lujan introduces the concept of “digital natives” that denotes categories of people born in the wake of social media platforms (3). This group of individuals is well equipped with knowledge regarding the operations of social media tools not only as interaction zones but also as facilitators of organizational performance. Digital natives have deployed their social media expertise to enhance various aspects that are deemed vital in organizations.
For instance, their daily interactions with peers via Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, and LinkedIn among other platforms have molded them into “optimistic and team-oriented achievers who are talented with technology” (Bondarouk and Olivas-Lujan 5).
It is interesting that excluding social media from today’s business operations may result in the total mal-functioning of practically all organizations. In addition to facilitating the tracking of institutional activities, social media tools have helped to enhance security measures to ensure that issues related to cybersecurity are addressed appropriately (Belangee et al. 122). Hence, in line with Bondarouk and Olivas-Lujan’s perspectives, having a technologically perceptive workforce is an inevitable endeavor in contemporary organizations that rely on social media to run their affairs (5).
Social media platforms have played a huge role in marketing countries’ political drives. In a study by Safiullah et al., present-day democracies have realized the impact that social media avenues, particularly Twitter and Facebook, have in influencing political outcomes of various candidates (10). The selection of these two platforms to serve political agendas is founded on the awareness that they have a huge global audience to the extent that a single candidate can have millions of followers in their respective Twitter and Facebook accounts.
In particular, a country such as India whose population is beyond 1.2 billion has close to 200 million citizens registered in various platforms (Safiullah et al. 11). Social media has shifted from being limited to the running of organizational affairs to being deployed as an effective framework that has been tested and confirmed to shape election results in many countries around the world.
The article by Safiullah et al. provides cases of countries that relied on various platforms to boost their candidates’ success in politics (11). For instance, famous American political campaigns of 2008 and 2016, New Zealand’s voting processes of 2011, and those of Sweden in 2010 confirm that social media tools have the potential of determining the next president of a particular country. They help in assessing and establishing public judgment.
Although many cases of the positive influence of social media on politics have been documented, the study by Safiullah et al. singles out the 2014 Indian political campaign whereby the country’s current Prime Minister, Narendra Modi, clinched this seat, thanks to his huge social media fan base. During this heated electioneering period, close to 30 million Indian citizens made approximately 230 million election-based proceedings in the form of “posts, comments, shares, and likes” (Safiullah et al. 11).
Specifically, out of all candidates running for this esteemed position, Narendra Modi secured the audience of more than 80 million Indians, with almost 14 million of them following him closely via his respective social media platforms. Hence, it is apparent that analyzing the contemporary political environment may not be exhaustive without a mention of the role of social media in influencing various outcomes. Nonetheless, from an individual and societal perspective, it has had its share of drawbacks based on its capacity to erode morals.
Cons of Social Media
Despite the fact that the world of business and politics has benefited substantially from social media, it is worrying that the same mechanism has contributed to the erosion of personal and societal morals. From a personal perspective, social media has opened the way for people to consume immoral contents from the comfort of their rooms where no one else watches or can sound an alarm to stop the practice. Although the study by Stevens et al. does not explicitly mention the issue of pornography among individual users, it is implied that many adolescents, particularly college learners, have been exposed to such sexual-related contents because of social media (61).
Almost all students have access to tablets or smartphones. However, such tools have been deployed to serve immoral purposes that are fueled by users’ access to the Internet, which they deploy to install various social media applications.
Although the original idea of having the above gadgets is to facilitate their learning under the watch of responsible people such as parents or teachers (Wang and Xing 186; Martin et al. 213), Stevens et al. reveal that indeed those who are left to enjoy social media freedom end up ruining their morals through the consumption of pornographic contents (62). Considering a case of an individual user posting personal information accidentally that ends up attracting media uproar, the rate at which it spreads has the potential of interfering with the particular individual’s self-esteem.
A teenager with such low levels of self-confidence may resort to consuming negative social media materials. In the article by Martin et al., “Twenty-two percent of boys (compared to 6% of girls) reported having searched the topic of sex on the Internet and roughly, 40% of both boys and girls reported having encountered sexually inappropriate material on the Internet” (213). Since behavior is created through a repeated exercising of a particular habit, it is possible that the continued consumption of such materials through various social media platforms is sufficient to ruin their individual morals and, consequently, their future lives.
Social media has contributed significantly to a society that is characterized by mentally sick youths following their extensive exposure to illegitimate materials. According to Martin et al., adolescents who spend more than four hours in a week on various platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, or WhatsApp have heightened chances of developing gloominess and social seclusion (213). The implication here is that social media breaks teenagers’ physical socialization skills. Being technically separated from the world because of the excessive utilization of negative social media contents is a precursor to worse behaviors such as suicidal attempts among youths. In almost all societies, young people take the largest share of the population.
In this regard, having the majority of teenagers experiencing anxiety and seclusion implies a community whose future is at risk. Brailovskaia and Margraf (1) conducted a study that confirms findings by Martin et al. (213).
These authors introduce the issue of Facebook Addiction Disorder (FAD) that has been manifested in many young people in the society (Brailovskaia and Margraf 1). From this study’s results, FAD had a negative bearing on social media users’ psychological conditions following its contribution to nervousness, hopelessness, and trauma (2). Because this study finds that young people are at a higher risk of developing negative behaviors that may ruin their future if their social media consumption is left unaddressed, it is crucial to examine the role that parents can play in ensuring that their children use Internet-facilitated platforms constructively. However, this issue will be examined later in this paper.
Another con of social media revolves around its capacity to ruin marriages. Many families wish to have their affairs kept secret, regardless of whether they are positive or negative. Although the study by Cravens et al. does not directly reveal family break-up matters, it indicates a situation where the publicizing of marriage affairs using social media may result in separation among couples because classified information finds its way to the wrong audience (372).
Cases have been reported of couples who have encountered sex-related materials in their respective partners’ social media accounts. Mainiero and Jones paint a worrying picture of unfaithfulness demonstrated by co-workers to the extent that one can exchange pornographic materials or solicit sexual affairs from married people using social media tools such as Facebook or WhatsApp (367). Once the “faithful” partner notices such hidden issues going on in social media platforms, chances are high that the particular marriage is destined for falling. From another perspective, social media has been used to facilitate sexual harassment.
Many workers have been sexually molested at least once in the workplace. Such practices have a bearing on marriage breakdowns because they lead to “decreased job productivity, increased stress, absenteeism and tardiness, and turnover” (Mainiero and Jones 368). In this case, having one’s income cut following immoral social media proceedings can result in family conflicts because of unfulfilled financial demands before ultimately culminating in divorce.
It is apparent in this paper that young people who take the largest share of social media consumers are the biggest losers, despite the overall finding that Internet-facilitated platforms may be the future of the world of business and politics. In addition to social media consumption subjecting them to psychological ailments, they have had their behaviors, education, and, consequently, their upcoming lives interrupted.
An earlier study by Wang and Xing indicated high levels of laxity among parents (186). A recommendation that can be made from this article revolves around the need for parents to closely monitor what their children consume in various social media platforms. The issue of securing them smartphones and sources of Internet and failing to supervise their daily social media engagements paves the way for counterproductive practices.
Hence, for youths to deploy social media tools to achieve constructive goals such as learning, it is crucial for parents to ensure that applications installed in their children’s devices do not create avenues for content abuse. In addition, constantly mentioning to teenagers that social media has the potential of influencing one’s life positively, especially when constructive contents are retrieved and consumed, may encourage them to utilize various platforms for learning purposes. This way, they will contribute to the overall claim that Facebook, WhatsApp, Twitter, and Instagram among others are not only efficient marketing tools but also effective family relationships boosters.
Conclusion
Social media tools have led to the establishment of virtual business networks and communities whereby people can communicate, exchange opinions and images of various items, or even share audio and video contents with others who may be geographically situated in distant places. Such a manner of operating was not impossible during the pre-social media era because individuals were only limited to interacting with others who seemed close or physically accessible and probably known to them.
It also took extensive time, energy, and financial resources for such operations to be fulfilled. Social media has opened up avenues for individuals to network without necessarily spending more time or money, having to meet with one another, or even moving from the comfort of their rooms to deliver particular messages. Nonetheless, it has been almost impossible to control things that users share on social media, including the rate at which they spread to almost every part of the globe within seconds.
It has also been troublesome to ensure that children are not subjected to contents beyond their ages such as pornographic materials or any other sensitive information. Based on the expositions made in this paper, parents have a key role to play in ensuring that children use social media platforms constructively, for instance, as tools for facilitating their learning processes or enhancing their family relationships. This way, they will stand a better chance of tapping the potential that such avenues have in shaping people’s future and current lives.
Works Cited
Baum, Mathias, and Rüdiger Kabst. “The Effectiveness of Recruitment Advertisements and Recruitment Websites: Indirect and Interactive Effects on Application Attraction.” Human Resource Management, vol. 53, no. 3, 2014, pp. 353-378.
Belangee, Susan, et al. “Cybersocial Connectedness: A Survey of Perceived Benefits and Disadvantages of Social Media Use.” Journal of Individual Psychology, vol. 71, no. 2, 2015, pp. 122-134.
Bondarouk, Tanya, and Miguel Olivas-Lujan. Social Media in Strategic Management. Emerald Group Publishing Limited, 2013.
Brailovskaia, Julia, and Jürgen Margraf. “Facebook Addiction Disorder (FAD) Among German Students—A Longitudinal Approach.” PLoS ONE, vol. 12, no. 12, 2017, pp. 1-15.
Cravens, Jaclyn, et al. “Why I Stayed/Left: An Analysis of Voices of Intimate Partner Violence on Social Media.” Contemporary Family Therapy: An International Journal, vol. 37, no. 4, 2015, pp. 372-385.
Garrido-Moreno, Aurora, and Nigel Lockett. “Social Media Use in European Hotels: Benefits and Main Challenges.” Tourism & Management Studies, vol. 12, no. 1, 2016, pp. 172-179.
Mainiero, Lisa, and Kevin Jones. “Workplace Romance 2.0: Developing a Communication Ethics Model to Address Potential Sexual Harassment from Inappropriate Social Media Contacts Between Coworkers.” Journal of Business Ethics, vol. 114, no. 2, 2013, pp. 367-379.
Martin, Florence, et al. “Middle School Students’ Social Media Use.” Educational Technology & Society, vol. 21, no. 1, 2018, pp. 213-224.
Olivas-Lujan, Miguel, and Tanya Bondarouk. Social Media in Human Resources Management. Emerald Group Publishing Limited, 2013.
Safiullah, Md, et al. “Social Media as an Upcoming Tool for Political Marketing Effectiveness.” Social Media and Marketing Effectiveness, Asia Pacific Management Review, vol. 22, no.1, 2017, pp. 10-15.
Stevens, Robin, et al. “Social Media in the Sexual Lives of African American and Latino Youth: Challenges and Opportunities in the Digital Neighborhood.” Media & Communication, vol. 4, no. 3, 2016, pp. 60-70.
Wang, Xianhui, and Wanli Xing. “Exploring the Influence of Parental Involvement and Socioeconomic Status on Teen Digital Citizenship: A Path Modeling Approach.” Educational Technology & Society, vol. 21, no. 1, 2018, pp. 186-199.
