Abstract
The consumption of fast food among people of different age has become one of the most discussed issues. The present study aims at defining the key factors that impact fast food consumption to broaden the perspective of students in New Zealand and local fast food producers and learn more about customer behavior. Based on considerations related to data accuracy, the researchers decided to rely on quantitative data analysis methods that allow comparing the reasons to consume fast food in terms of their popularity.
The study reports the results of the survey that includes ten questions. The sample is presented by fifty international students in Whitireia New Zealand. The data was coded and presented with the help of pictorial diagrams and graphs. The results indicate that respondents spend less than $10 on fast food at a time. The majority of students prefer eating American fast food such as hamburgers. The research shows that the primary reasons to consume fast food are convenience, gustatory qualities, and a lack of time. The results can be used to strengthen the marketing strategies of local fast food producers and conduct further research to study the extent to which cultural background and heritage impact the key reasons why people consume fast food.
Introduction
With the acceleration of people’s living pace, eating out becomes more and more people’s choice, especially fast food, which is the most important reason for people to choose fast food. The roots of fast food come from North America, where people often eat out and have a much more hectic lifestyle. (Global fast food market – industry analysis, size, share, growth, trends, and forecast, 2013 – 2019. (2014, Jun 11). According to statistics (Austin, S. B., Melly, S. J., Sanchez, B. N., Patel, A., & al, e. (2005).
In the past three decades, fast-food retail sales in USA has soared 900% from $16.1 billion in 1975 to $153.1 billion in 2004.(Fast food smarts: New design of fast food carrier bag civilises the eating experience by turning into a tablecloth; fast food smarts: New design of fast food carrier bag civilises the eating experience by turning into a tablecloth. (2004, Jul 19). The fast-food industry now has more revenue than restaurants.
The office workers may face more time pressure from the work, affordable prices and popular everyday meal options, the main reason for they choose fast food. Blue-collar workers may be engaged in non-standard working hours (e.g., shift work), a fast food restaurant convenient purchase location and catering services at any time (unlike the only open restaurant in fixed time) is why they choose the fast food is higher. In short,Because of time constraints, convenience, and lifestyle, fast food has become an increasingly important part of the people diet. As part of the global diet culture, fast food has a great variety of tastes and tastes.
By geographical classification, the fast food market has been divided into North America, Europe, the Asia-pacific region. Fast food chains and regional Quick Service Restaurants have customized their format and menu offering according to various regions as preferences of people and taste differ from place to place. The types of fast food products are mainly divided into:Subway /Burger/Sandwich Pizza/Pasta Chicken Asian/Latin American Food Sea-Food Others (Snacks, Mexican etc) As a nation of immigrants, the fast food market in New Zealand covers almost the major fast food categories in the world.
This research analyses and summarizes the fast food market of the international students (sample survey) of WHITEIRE in the form of questionnaire survey. This study will be explored to answer the following research questions in order to achieve the research objectives, which are:What are the factors impacting on customer choice for fast food? For entering the local fast-food industry merchants to provide certain reference basis in the market, but also for consumers (mainly international students) to provide more fast food information, enrich their food culture (not just limitation the types of their country’s fast food).
Literature review
The development of the human society is closely interconnected with economic growth and the creation of new technology, and it has a major influence on the tastes and preferences of students and employees in different fields of activity. People from these social groups are required to be productive and make decisions as fast as possible, and it is believed that these changes related to the rhythm of life have contributed to the popularity of fast food.
The given paper aims at expanding the knowledge concerning the factors that encourage customers to give preference to fast food. The review of the most recent scholarly articles on the topic of factors that encourage people to consume fast food indicates that modern researchers have different opinions concerning the issue, and additional research is needed to study the factors that impact international students in New Zealand.
To begin with, there are many studies that support the idea concerning the pivotal role of affordability in fast food consumption among people from different age groups. In their research, Eckert and Vojnovic (2017) list affordability and the low paying capacity of the population among the key factors that encourage fast food consumption in people of different age. Nevertheless, it needs to be taken into account that the sample was impacted by unfavourable socio-economic conditions.
The opinion concerning the connection between price and the attractiveness of fast food is supported by Mai (2016) who proves that purchasing decisions of fast food consumers among students are highly impacted by affordability. The connection between the prices of fast-food meals and customers’ purchasing intentions is also emphasised in the work by Martins, Rindova, and Greenbaum (2015) who support the willingness of fast food producers to rely on affordability to increase their competitive advantage.
Apart from the price of fast food in comparison with other types of food, modern researchers pay focused attention to personality traits when analyzing the factors that impact fast food consumers. For example, Garza, Ding, Owensby, and Zizza (2016) suppose that increased fast food consumption can be attributed to certain psychological characteristics of consumers such as impulsivity. Even though the role of psychological traits in connection with fast food consumption is not among the most relevant research questions, this opinion is supported by another research. The study by Folkvord, Anschütz, Boyland, Kelly, and Buijzen (2016) argues that impulsive children are more likely to prefer fast snacks.
Another factor that is believed to be responsible for the growing popularity of fast food is convenience and the gustatory qualities of fast food. The study by Garza et al. (2016) also states that convenience is perceived as the key reason why people prefer fast food. DeVoe, House, and Zhong (2013) believe that the popularity of fast food is primarily caused by the opportunity to save time that exists for consumers. Also, Zagorsky and Smith (2017) state that people who do not have enough free time tend to prefer fast food due to its convenience.
Methodology
Fast food is especially popular in the group of teenagers, who visit the fast food restaurants around twice a week on average(Paeratakul, S., Ferdinand, D. P., Champagne, C. M., Ryan, D. H., & Bray, G. A. (2003). Therefore, as consumers of the fast food industry, the fast-food restaurants around the campus are especially dense. According to the analysis(Austin, S. B., Melly, S. J., Sanchez, B. N., Patel, A., & al, e. (2005).
The number of fast-food restaurants, which are less than 1.5 kilometres from the school, is three to four times the number of restaurants in the vicinity of the city that are not affiliated with the school. The middle distance from any school to the nearest fast-food restaurant is half a kilometre, which shows that in half of the schools, it means the students need to walk more than five minutes to reach a fast-food restaurant.
This study will be explored to answer the following research questions in order to achieve the research objectives, which are:What are the factors impacting on customer choice for fast food?
This study mainly uses Quantitative method to collect data. Quantitative research is ‘Explaining phenomena by collecting numerical data that are analysed using mathematically based methods (in particular statistics)’.
Therefore, this subject is more suitable to answer in a quantitative way. The particular questions seem immediately suited to being answered using quantitative methods.
Sampling methodology
This paper mainly adopts the form of questionnaire survey from fifty international students in Whitireia Community Polytechnic Auckland campus were invited to participate in the survey. In line with, non-probability the theory of convenience. The location of answering the questionnaire in the campus are study skills center, library and lobby. The subject of investigation is:survey on fast food consumption choice. There are 10 questions in total,including three of the demographic questions(Gender,age and nationality)and seven of the relevant closed questions to survey。
Data collection
This study complied research ethics:topic of survey ,objectives are stated,and For whom the survey was conducted and by whom it was carried out. To make clear the names of those who carried out the survey are stated。sampling frame is specified for international students in W campus。Steps taken to ensure that the sample design would actually be carried out to independent. Participants completed the questionnaire independently without any interference (such as group discussion, or other reference answers).
Obviously the questionnaire was designed within 10 questions. They include three of demographic questions(Gender,age and nationality)and seven questions were related with closed. All meet the requirement of questionnaire survey format:frequency ,species, influence factor ,price range,mostly way(takeaway or eat in sore) and interval(Do you agree fast food can represent a countrys culture?)
This survey, conducted on Friday morning and collected data in the form of questionnaires from 50 international students,Response rate:100%. But only 46 could be used as data analysis, the reason is Q2 in the questionnaire :What kind of fast food do you mostly consume? And Q4:Which of the following, do you think, is the #1 factor that influences your fast food consumption? To be asked for just choose only one. But these two questions offer more than 10 questions,so the investigators had multiple choices in response. In order to solve this initial design problem at the beginning. At once, please choose only one in Q2 and Q4 to use the highlight and bold to remind those participants.
Thereby,collected data from these samples sufficiently big enough to reliably perform intended tests and implications.
Data analyses
Mainly through statistical tests used in data analysis。Firstly, coding of the collected data. And divide them into different categories as tables,figure and pie to illustrate. For instance, three questions of demographic were used in pie to analyse or graph to states. The purpose of this research is to provide a clearer overview of the underlying situation of the investigator (consumer). And use tables are parting for Q1, Q3 and Q5 to analysis and summarize, it is a basic overview of consumer behaviour.
Lastly, to analyse the form of Q2, Q4 and Q6 as figure,because of these are two key issues for fast food. Moreover, there are more than 6 options and figure out the analysis results by using alone. Since the Q7 is in the form of interval, therefore to state it in the pie chart. All-important findings are explained in different variables and explained in the results of this report.
Results
This study takes statistical tests used for data analysis, and describes the results through tables and graphs.
Firstly, from the demographic questions, it can be seen the overview of participants. The proportion of female is about twice times that of male. The age group of 20 to 30 years old is the largest percentage, reach at 30 persons. Among all the 46 responders from 12 countries, particularly the Chinese students are the most with 17, the next number of students are Indian, at 14. There are only three students in New Zealand and Sri Lanka, two persons in Korea, Brazil and Tonga. And the only one in Vietnam, Filipinas, Nepal, Germany and Hong Kong respectively. All in all, the main overseas students come from China and India.
Secondly, it also states that the frequency of eating fast food groups is still relatively high, half of the customers are sometimes.
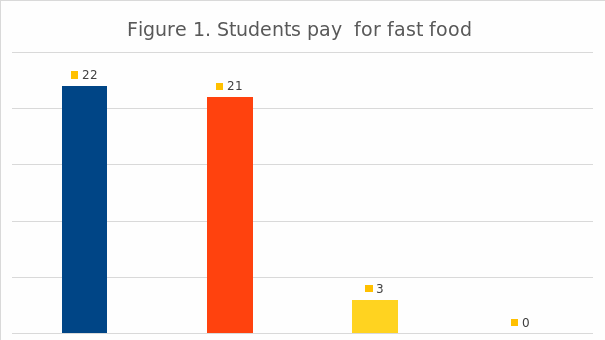
Students pay for fast food.Figure 1 displays the price less than $15 is the most common among students pay for fast food. Similar percentage between the price of less than $10 and that of $10 to $15, more than 20 students to choose. Nobody chose the price of above $20. This price positioning for the fast food industry has a very useful reference value.
Form the Q5 of questionnaire, it can be depicted that because of convenience and speed of fast food, students prefer to pack rather than eat at the store. This is also a lot of fast food restaurants prefer the form of convenience stores, providing a small amount of dining tables and chairs to package as the main mode.
Table 1. How do the students agree fast food can represent a countrys culture?
Table 1 illustrates the considerable students were strongly agree with this view, through the diet to understand other cultures. In other words, fast food culture is also one of the ways of cultural diversity. This section is an extension of the fast-food industry survey, that is to say fast-food can represent a country’s culture: East-West diet, eating habits of different religious ethnic groups.
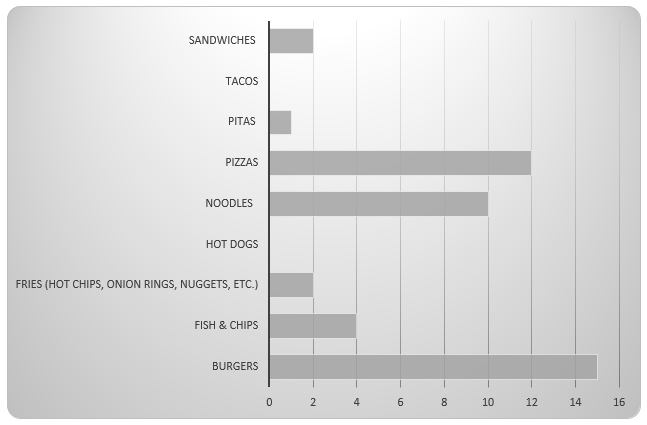
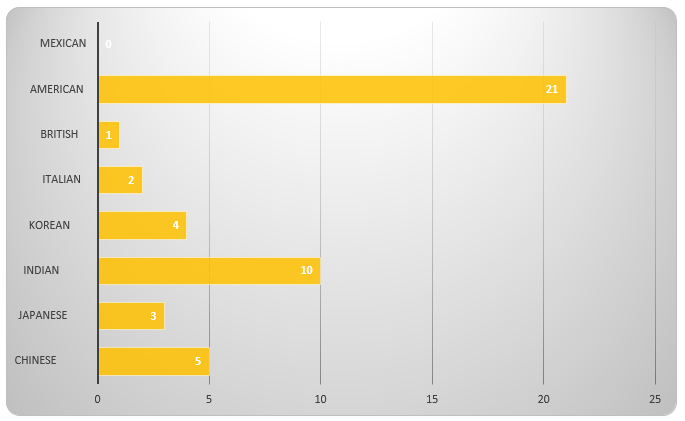
Figure 3. Which country`s fast food do students eat most.It is notable that, there is a little bit similar with the Figure 2 and Figure 3.Both of them are talking about the type of fast food survey. However, the difference is the respondersfavourite food and the food which is eaten frequently. The point of the issue is to explore consumers’ specific preferences for the type of fast food. According to analysis, it can be stated that nearly half of students often eat American fast food, favourite type of eating is Hamburg. Therefore, it can determine the consumer preferences among international students.
Table 2. #1 factor that influences students’ fast food consumption.
In terms of the first factor affecting consumers’ choice of fast food is especially important for the market development of the fast food industry. From the analysis, it can be indicated that convenience is the most essential factor, which is significant important for the location of fast food restaurants. That is why a large number of fast food restaurants can be located near schools and companies, easier to find the target consumer groups, and to provide them with fast and convenient Catering service.
The second factor influencing consumer behaviour is taste. Obviously, students from different countries have different tastes. Interestingly, the impact of the price factor (affordability and promotions) on consumers is minimal in this section. In other words, the market positioning of the fast food industry has a certain degree of stability, below $15 of one meal is the mainstream trend.
Conclusion
The study aims at defining the factors that impact the consumption of fast food in New Zealand. The majority of respondents are from China and India, and their age varies from twenty to thirty years old. In reference to the key findings, the data analysis indicates that the majority of respondents spend less than 10$ on fast food. Despite an evident affordability of fast food for international students, only one respondent considers affordability to be the primary factor that impacts his or her choice.
The survey that was conducted within the frame of the study shows that factors whose influence on the respondents’ purchase decisions are presented by convenience and taste. Apart from that, more than 19% of respondents indicate that being pressed in time is the primary reason why they choose fast food. In general, these findings align with these reported in the most recent studies by other researchers.
The study has limitations as the given number of research participants does not allow making definitive conclusions on the problem and some factors mentioned by students are ambiguous. Nevertheless, the results can be used by fast food producers and researchers in New Zealand who are interested in perceived benefits of fast food. The retrieved data can provide the basis for new marketing strategies and research that is aimed at studying the interconnection of these factors and cultural background.
References
DeVoe, S. E., House, J., & Zhong, C. B. (2013). Fast food and financial impatience: A socioecological approach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 105(3), 476.
Eckert, J., & Vojnovic, I. (2017). Fast food landscapes: Exploring restaurant choice and travel behavior for residents living in lower eastside Detroit neighborhoods. Applied Geography, 89, 41-51.
Folkvord, F., Anschütz, D. J., Boyland, E., Kelly, B., & Buijzen, M. (2016). Food advertising and eating behavior in children. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 9, 26-31.
Garza, K. B., Ding, M., Owensby, J. K., & Zizza, C. A. (2016). Impulsivity and fast-food consumption: A cross-sectional study among working adults. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 116(1), 61-68.
Mai, P. H. (2016). Determinants impacting consumers’ purchase intention: The Case of Fast Food in Vietnam. International Journal of Marketing Studies, 8(5), 56.
Martins, L. L., Rindova, V. P., & Greenbaum, B. E. (2015). Unlocking the hidden value of concepts: a cognitive approach to business model innovation. Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, 9(1), 99-117.
Zagorsky, J. L., & Smith, P. K. (2017). The association between socioeconomic status and adult fast-food consumption in the US. Economics & Human Biology, 27, 12-25.
